The magazine with greatest impact in the Physics field, “Reviews of Modern Physics”, has chosen an article wrote by the scientists of the Instituto de Física Corpuscular (IFIC, CSIC-Universitat de València) José Bernabéu Alberola and Fernando Martínez Vidal for its last cover.
The article, entitled “Time-reversal violation with quantum-entangled B mesons” is one of the conferences of “Reviews of Modern Physics (RMP)” one of the magazines of “Physical Review”, belonging to the American Physics Society (APS). Its review articles offer a deep treatment of a research area, reviewing recent works and relevant articles and providing an introduction for postgraduate students and researchers from other related areas.
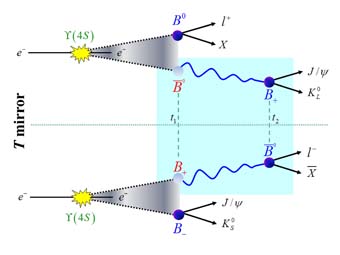
Shorter conferences, describe recent work of general interest in the frontier of physics with impact in several different fields. For this publication, one of the highest internationally impact ahead of 'Nature' and 'Science', the authors have included a figure IFIC, now chosen for the cover of the magazine, illustrating the basics of the experiment that has shown directly and with a high level of significance breaking the temporal symmetry in the fundamental laws of Physics.
This choice reflects the impact of this work, done by the BABAR collaboration International Laboratory SLAC (Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, USA) and published in late 2012 in the journal “Physical Review Letters”. The study, proposed and led by scientists at CERN, was selected by the editors of the magazine as “Viewpoint in Physics”. Only a hundred out of 18,000 articles published annually by the APS are elected.
Other publications such as “Physics Today”, Nature”, “The Economist” and “Physics World” published articles and reviews on this outcome. This last one, which prepares annually investigations considered Top 10 Physics of the year, selected this results in the third position in 2012. The first position was occupied by the discovery of the Higgs boson by the experiments ATLAS and CMS at CERN.
The symmetries, or lack (rupture) of them are a cornerstone for understanding the fundamental laws of nature. One of the most important symmetries, but also the most difficult to detect directly in the laboratory, is the time reversal. We say that there is symmetry under time reversal if the same physical laws are valid for both a sense of movement to its inverse, which is to say that work the same forward and backward in time.
This has no relation with the arrow on macroscopic time, so familiar in everyday life, but affects the quantum laws that govern the microscopic world. For an isolated particle, over the same time seems forward and backward, that is, their movement is symmetrical reversible or temporarily. However, this symmetry is broken in certain physical processes, such as what it was observed with B mesons, a particle composed of a quark of type b (called “beauty”) and an antiquark type d (named “down”) by the BABAR experiment in November 2012. This asymmetry is closely linked to one of the most enigmatic properties of nature, the difference between matter and antimatter.
Direct observation of temporal asymmetry was made possible by the unique ability of the experiment to produce entangled pairs of B mesons. Two particles are entangled when their quantum properties are not independent of each other, even if they are spatially separated. This phenomenon, one of the most amazing of quantum mechanics, was introduced long as a paradox (known as the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen, or EPR).
Today, experimentally proven, its use is widespread in various fields such as information and quantum computation. In this experiment is used so that when measuring the state of one of the B mesons can infer the status of your partner. This made possible to compare some transitions between pairs of states of b mesons with their inverses and see that transitions do not occur in the same way.
For more information:
‘Colloquium: Time-reversal violation with quantum-entangled B mesons’, J. Bernabéu and F. Martínez-Vidal. Rev. Mod. Phys. 87, 165 – Published 23 February 2015.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.87.165
Cover of Reviews of Modern Physics magazine: http://journals.aps.org/rmp/
To find out more about it: ‘Panorama: Ruptura de simetría bajo inversión temporal’, J. Bernabéu y F. Martínez Vidal. Investigación y Ciencia. Octubre 2013.
Last update: 27 de february de 2015 07:51.
News release


















