Conferències al DAA. Xarrada a càrrec de l'investigador Tomasz Rembiasz, del Departament d'Astronomia i Astrofísica (UVEG). Lloc: Seminari del Departament d'Astronomia i Astrofísica, 4a planta de l'Edifici d'Investigació, a Burjassot. Dia: divendres 11 de març de 2016. Hora: 10:00.
Abstract
The magnetorotational instability (MRI) is one of the most promising agents
amplifying the magnetic fields in a core-collapse supernova (CCSN) explosion. It was suggested that the MRI can be terminated by developing on top of the MRI structures parasitic instabilities of the Kelvin-Helmholtz (KH) or tearing mode (TM) type. We find that depending on the numerical setup, the MRI can be indeed terminated by KH instabilities or (driven by numerical resistivity) TMs.
The latter, however, being unphysical under the CCSN conditions should be avoided in CCSN simulations. We study under which numerical conditions TMs driven by numerical resistivity can develop. We find that in MRI simulations with sufficiently low physical dissipation, MRI is terminated by KH instabilities (as theoretically expected for the CCSN conditions) and that the MRI can amplify the initial magnetic field only by a factor of the order of ten.

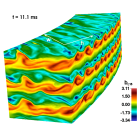
Snapshot of the evolution of the radial component of the magnetic field (in units of 1e15 G) in a local simulation with conditions representative of the existing in the outer layers of a protoneutron star. The snapshot it taken 11.1 milliseconds after set
Llista d'enllaços: