
by Andrés Rubio
1. What is a wave?
Have you ever tried to throw a stone into a lake? Probably yes. What happens when you do it? Exactly, there appears a circle which moves in all direction making itself bigger and bigger. In Physics, when we make a system that was quiet suddenly change, we say that we perturb the system. So, when you throw that stone you are creating a perturbation.
So, that what a wave is: a perturbation that propagates in the space. Or, in a more accurate way:
A wave is a propagation of Energy which carries no matter.
A wave carries no matter because if it would, the amount of water in the lake would change, but, if you think about that, it never does.
Examples of waves are the light we see by our eyes, or the sound we hear by our ears.
2. Types of waves
Basically, we have two different kind of waves according on the direction of the perturbation that the wave carries.
3. Wave equation
If we want to work with waves in a proper way, we will need to know how a wave can be mathematically expressed. The equation of a wave has the following form:
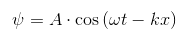
It is very useful because you can know the value of the perturbation in any time and position. It depends on three different parameters:
We can plot the equation to obtain:
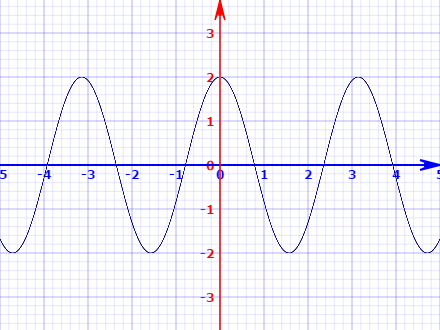
And we can observe that it has the shape of an oscillation.
4. Properties of the waves
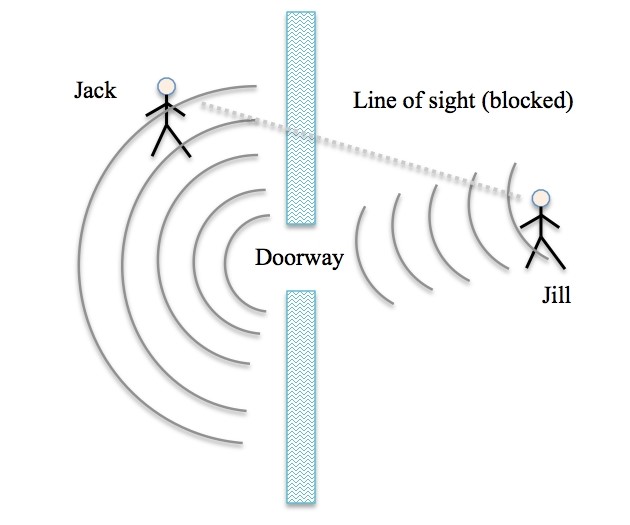
The waves, as we have said before, present some different properties than the properties of the common particles. Basically, there are four properties: reflection, refraction, diffraction.
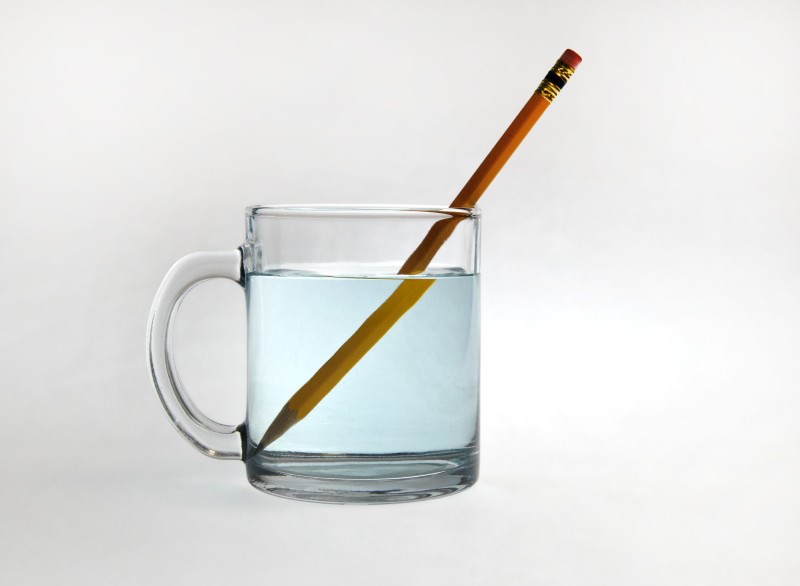

Image belonging to the Florida Center for Instructional Technology. University of South Florida.
Copyright © 2011-2017. Suitable for educational purposes.
In progress.
© Copyleft 2016, Content and Language Integrated Learning and ICT Group