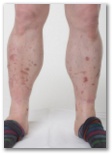
A 48 year old man with type 2 diabetes presented with a two year history of asymptomatic spots on his shins (fig 1). Examination showed multiple pretibial patches which were irregularly shaped, pigmented, and atrophic. A few similar lesions were seen on his forearms.
Diagnosis?- diabetic dermopathy
- necrobiosis lipoidica
- post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
- skin staining after antimalarials and quinolones
- ¿?
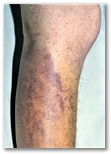
A 58 year old man presented with fatigue and perifollicular haemorrhages, bruises, and corkscrew-hairs on his legs (fig 1). His diet was meat based, with little intake of fruit or vegetables. There were no features of malabsorption.- thrombocytopenic purpura
- scurvy
- henoch schonlein vasculitis
- purpura senil

A 14‐year‐old Chinese boy was admitted because of the sudden onset of a painful rash over both lower extremities and mild abdominal pain. He was a hepatitis B carrier. He had a history of a similar but milder rash 2 years ago. The lesions then resolved shortly and no skin biopsy was performed. Before this episode, he had a sore throat and running nose for 3 day. After admission, the skin lesions worsened. Apart from a few palpable purpuric lesions, tender tense vesicles and bullae with turbid content dominated the clinical picture
Laboratory investigations including complete blood analysis, clotting profiles, liver, and renal function tests, complements 3 and 4 and antistreptolysin O were all within normal limits. Urinalysis and stool analysis had negative findings. A throat swab for viral culture and serologic titers for herpes simplex virus also gave negative results. A skin biopsy specimen showed leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a perivascular neutrophilic infiltrate, leucocytoclasia, and fibrinoid necrosis affecting the upper dermal venules, resulting in their destruction. However, neither IgA nor C3 deposition was found in the immunofluorescence studies. Immunofluorescence staining and culture for herpes simplex virus were negative and Gram stain and culture of the turbid content revealed no pathogen.
diagnosis?- bullous pemphigoid
- churg strauss syndrome
- bullous henoch schonlein
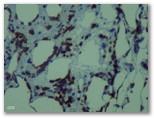 CD4
CD4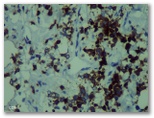 CD8
CD8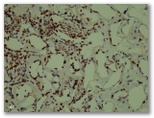 ki67
ki67
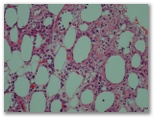
A 26-year-old man presented with high-grade intermittent fever with chills, weight loss, productive cough and episodic abdominal pain of 6 months duration. Physical examination showed that the patient was febrile with mild pallor. There were numerous, tender, erythematous, indurated nodules and plaques measuring 1–8 cm over the trunk (figure 1) and anterior aspect of the thighs. There were no ulcerations over the nodules and plaques. Small bilateral axillary lymph nodes were palpable.
Chest X-ray showed bilateral pleural effusion. The effusion was exudative with lymphocyte predominance and an elevated level of adenosine deaminase (ADA). Based on the above clinical presentation and investigations, pulmonary tuberculosis was considered and standard antituberculous treatment (ATT) was initiated. However, the ATT was stopped after 2 weeks as the high-grade fever persisted with significant increase in hepatic transaminase levels. Subsequently, biopsy of the indurated plaque over the trunk was performed,
DX. Tx?- cutaneous tuberculosis
- erythema induratum
- erythema nodosum
- another diagnosis
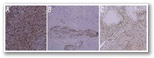 (A) diffuse positivity for cluster of differentiation (CD)34 and (B) smooth muscle actin expression in areas of myoid differentiation and (C) negativity for CD34.
(A) diffuse positivity for cluster of differentiation (CD)34 and (B) smooth muscle actin expression in areas of myoid differentiation and (C) negativity for CD34.
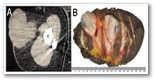
A 44-year-old woman presented with a recurrent mass on her right upper arm. The tumour had regrown since being surgically removed three years prior, At presentation, the lesion was attached to the overlying skin, measuring 8 x 7 x 6 cm. A computed tomography (CT) scan showed a homogeneously-enhancing soft tissue lesion in the subcutaneous plane of the lateral aspect of the middle-third of the right arm, measuring 7 x 6 x 4.5 cm [Figure 1A]. The lesion had well-defined margins except medially, where it was abutting the deltoid muscle with the loss of the intervening fat planes. However, CT scans of the chest, abdomen and head and neck region were normal.
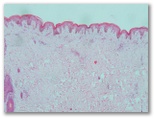
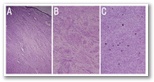
Upon gross examination, the excised soft tissue mass measured 13 x 11 x 5 cm. The surface of the lesion showed a firm homogenous polypoidal greyish-white growth of 6 x 6 x 4.5 cm, which extended deep into the underlying dermis [Figure 1B]. There were no areas of haemorrhage or necrosis. Histologically, the overlying skin was unremarkable. The tumour itself was located in the dermis and was composed of monomorphic spindle cells arranged in a storiform and fascicular pattern with a parallel arrangement of cells [Figure 2A]. In certain areas, the tumour was more cellular and composed of elongated cells with moderate cytoplasm and elongated-to-plump nuclei, which were mostly perivascular [Figure 2B]. The eosinophilic cells were bland-looking without pleomorphism or mitotic figures. The focal tumour cells contained brown intracellular pigment [Figure 2C]. The tumour had infiltrated the underlying soft tissue; however, all of the resected margins, including the circumferential resected margins and deep resection plane, were tumour-free. There was no evidence of mitosis, cellular atypia or necrosis.
An immunohistochemical panel of the tumour cells showed diffuse expression of vimentin and cluster of differentiation (CD)34 [Figure 3A]. The cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm showed immunohistochemical expression of smooth muscle actin, indicative of myoid differentiation [Figure 3B]. These areas were negative for CD34 [Figure 3C].- dermatofibrosarcoma protuberas
- undifferenteiated pleomorphic sarcoma
- atypica fibroxanthoma
- bernard tumor