ROSIS
 ROSIS
(Reflective Optics System Imaging Spectrometer) is a compact airborne imaging
spectrometer, which had been developed jointly by Dornier Satellite Systems
(DSS, former MBB), GKSS Research Centre (Institute of Hydrophysics) and German
Aerospace Center (DLR, Institute of Optoelectronics) based on an original design
for a flight on ESA's EURECA platform.
ROSIS
(Reflective Optics System Imaging Spectrometer) is a compact airborne imaging
spectrometer, which had been developed jointly by Dornier Satellite Systems
(DSS, former MBB), GKSS Research Centre (Institute of Hydrophysics) and German
Aerospace Center (DLR, Institute of Optoelectronics) based on an original design
for a flight on ESA's EURECA platform. 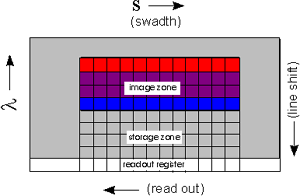 The detector chip is
a 2-dimensional CCD array (Thomson THX 7895). One dimension is used to scan
a narrow cross track line on the ground. The second dimension is for acquiring
the spectral information of each of these cross track pixels.
The detector chip is
a 2-dimensional CCD array (Thomson THX 7895). One dimension is used to scan
a narrow cross track line on the ground. The second dimension is for acquiring
the spectral information of each of these cross track pixels.ROSIS can be operated in different modes. This means that the user can select interesting areas (also dark references), lines or pixels on the detector array via PC programming. The mode configuration can be adapted to optimize the user's data needs. Some of these modi are used only for test or calibration purposes.
Spectrometer Characteristics
Wavelength range: 430nm - 850nm, bandwidth: min 15.2nm
84 bands in spectral mode, 32 bands in imaging mode
Main geometric parameters
Wavelength range: 430nm - 850nm, bandwidth: min 15.2nm
84 bands in spectral mode, 32 bands in imaging mode
Main geometric parameters
|
For more information, please visit the DLR's ROSIS Home Page