A research carried out by five laboratories in Seville, Logroño, Heidelberg (Germany) and Göteborg (Sweden) and led by the group of Yeast Functional Genomics (GFL) of the UV, has shown that the cells that live faster also accelerate their mechanisms of genetic regulation. The research, published in the journal Nucleic Acids Research, may be useful to achieve a greater understanding of the mechanisms that distinguish health from disease and design strategies for healing.
29 november 2016
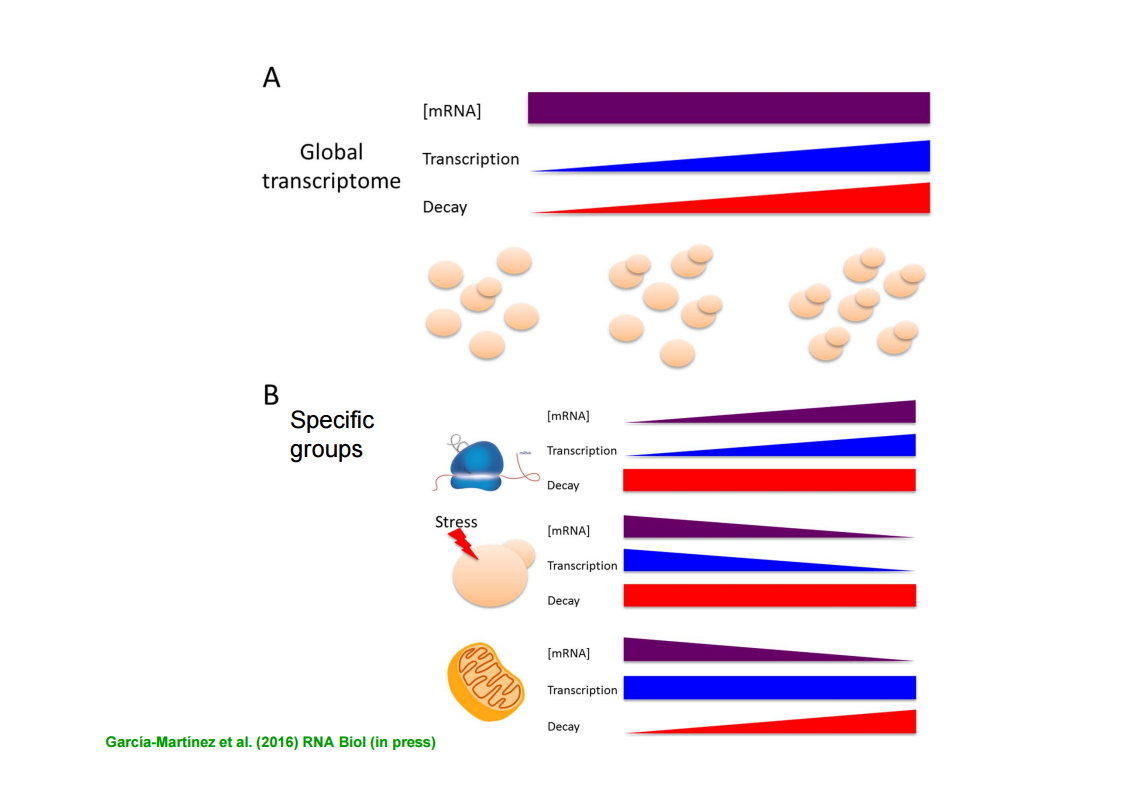
The genetic expression of eukaryotic cells, such as human or yeast cells, is not only dependent on specific regulatory mechanisms, but also on therate at which cells grow. In this research, scientists have taken as a model an eukaryotic beer yeast cell, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, to conclude that dependence of gene expression with growth rate is due to an acceleration in the turnover rate of messenger RNA (mRNAs) . Although the total concentration of messengers remains constant (homeostasis), mRNAs are produced and destroyed more rapidly. The conclusion is therefore that the cells that grow faster also live their gene expression faster.
In addition, researchers have observed that this global behaviour is not performed in some groups of genes that increase or decrease their turnover of mRNAs with the rate of growth. This is the case for genes related to mitochondrial respiration, for example, that decrease their expression by increasing the degradation of their mRNAs. Since it is a similar mechanism to cancer cells’ one, the research may be useful to explain how tumour cells, which grow much faster than healthy ones, regulate their genetic expression.This is why this basic research study will be a starting point to achieve in the futurea better understanding of the mechanisms that distinguish health from disease and the design of strategies for healing.
Due to the importance of its conclusions, this study has aroused a great interest in the scientific community. This is evidenced by the other two scientific reviews of the results published in large-scale journals in the field of molecular biology: Current Genetics and RNA Biology.