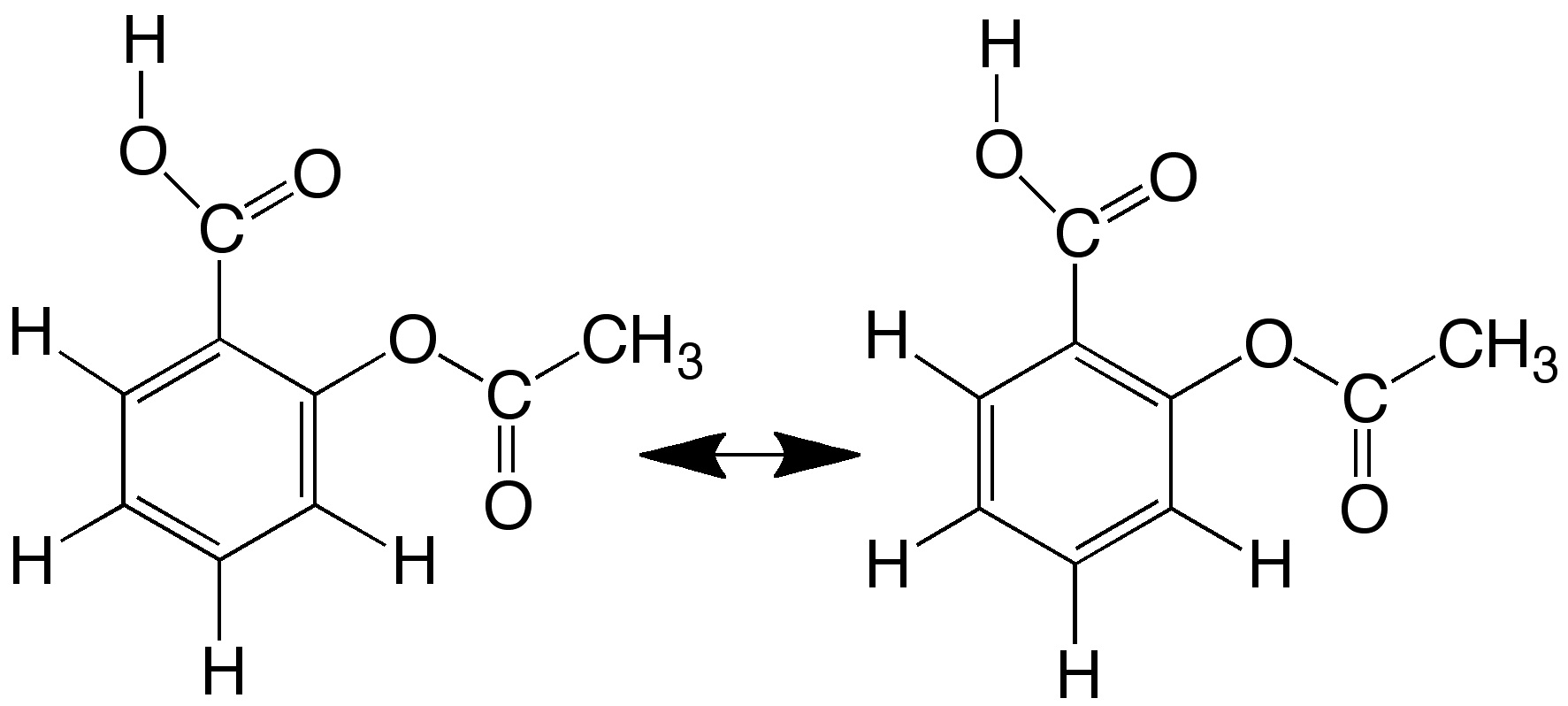
Salicylic acid, o-HO-C6H4-COOH,
has a benzene ring substituted by two functional groups, alcohol, HO-, and carboxylic acid,
-COOH, in ortho positions. The hydrogen atom of the alcohol group is substituted by an
acetyl group, CH3CO-. The benzene ring forms a system of conjugated double bonds
known as aromatic system . Although it is represented as alternated C-C and C=C bonds
this is only one of the two resonance forms.
The properties of the aromatic ring are different from compounds with separated C=C double bonds (olefinic).
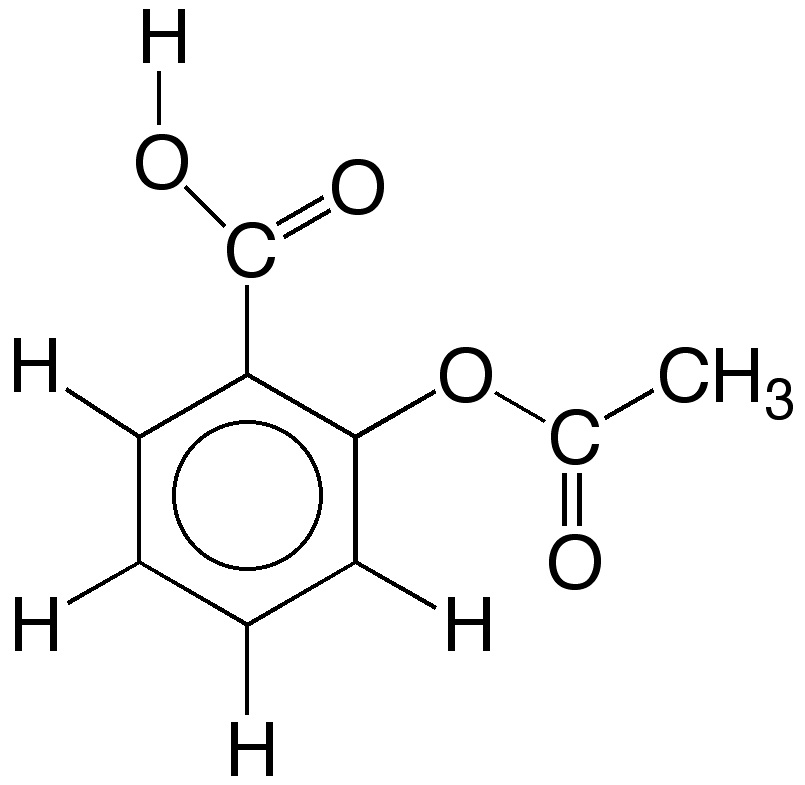
An alternative representation of an aromatic system is the replacement of the three double bonds by a circle, highlighting the
equivalence of C-C bonds in the ring.