Next: Seeing what is happening:
Up: Real time, control and
Previous: Real time, control and
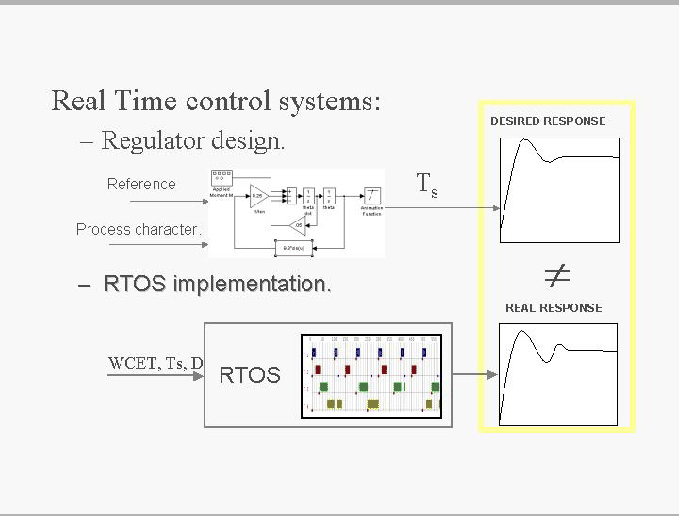
Real time control system are usually build in two phases:
In the first one, the regulator is designed by characterising the process and it is expected to obtain a desired response.
In the second, the regulator is implemented in a RTOS. It may happen that the real response doesn’t match with the desired.
The reason for this, can be found in the variable delays. They produce that the control actions can't be send at equal periods of time.
There are several things that causes variable delays like:
- Delays in control system.
- Delays due to sampling.
- Delays due to the use of computational resources. Caused either by tasks computing time and high priority task interference.
A task partitioning scheme for improve the control performances reducing the variable delay (Crespo et al., 1999) . This scheme splits system priorities into three bands:
- The final band with the highest system priorities.
- The initial band with the intermediate system priorities.
- The main band with the lowest priorities.
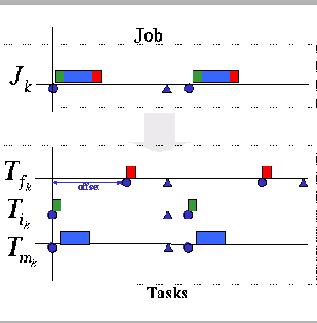
Following this scheme a periodic job can be split into three tasks: initial, main and final assigning a priority to each part in a the corresponding priority band.
Graphically, observe that for the final part an offset is added in order to execute it at same distance from activation.
The problem with this scheme is that increases notably the tasks in the system.
In order to solve the drawback before commented, two servers were proposed for initial and final bands with the following characteristics:
- Have a multiperiod resulting of all the tasks periods in a band
- Execute the activities of a singular task in each activation
- Apply the first come first served scheduling policy.



Next: Seeing what is happening:
Up: Real time, control and
Previous: Real time, control and
Josep Vidal Canet
2003-04-24