Next: 4.5 Multidimensional problems Up: 4 Métodos en diferencias Previous: 4.3 A standard implementation
Most ``conservation laws" include source terms (ex: relativistic hydrodynamic equations)
| (119) |
Two basic ways of handling source terms:
This algorithm can be improved by introducing succesive sub-steps to perform the time update (ex: predictor-corrector, Shu & Osher's conservative high order Runge-Kutta schemes)
![]() (Godunov splitting, first order)
(Godunov splitting, first order)
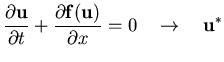
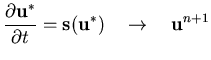
to get second order accuracy (assuming each independent method is
second order) ![]() Strang splitting:
Strang splitting:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
source transport source
Stiff source terms: model phenomena which
![]() lead to numerical difficulties
lead to numerical difficulties
the chemical reactions (or nuclear
reactions in stars) occur on much faster time scales than the gas flow
![]() waves may propagate at nonphysical speeds
waves may propagate at nonphysical speeds
Model problem: two chemical species, ``unburnt gas" and "burnt gas"
unburnt gas
![]() burnt gas
burnt gas
![]() : reaction rate
: reaction rate
![]()
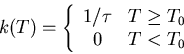
![]() : ignition temperature
: ignition temperature
![]() : time scale of the chemical reaction
: time scale of the chemical reaction
Equations:
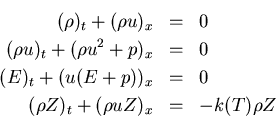
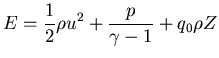
![]() : mass fraction of the unburnt gas
: mass fraction of the unburnt gas
![]() : adiabatic exponent
: adiabatic exponent
![]() : heat release
: heat release