Primera | Imagen anterior | Imagen siguiente | Última | Miniaturas
Bardhan A, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Chapple ILC, Fine JD, Harper N, Has C, Magin TM,
Marinkovich MP, Marshall JF, McGrath JA, Mellerio JE, Polson R, Heagerty AH.
Epidermolysis bullosa. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020 Sep 24;6(1):78.
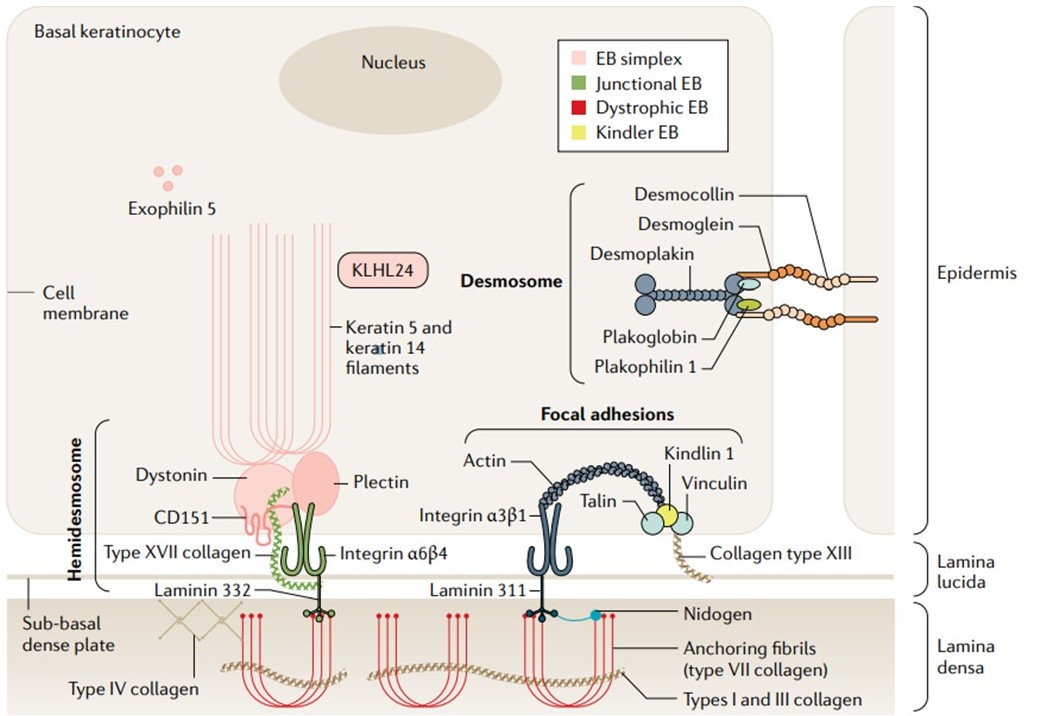
The cutaneous dermal–epidermal junction. Keratins 5 and 14 are produced in the basal keratinocyte and interact to form obligate heterodimers; compacted into intermediate filaments, these proteins confer tensile strength via a mesh-like cytoskeletal network. Intermediate filaments attach to hemidesmosomes (via inner plaque proteins) asymmetrically situated on the basal surface of the keratinocyte. KLHL24 is as a substrate adaptor for ubiquitin E3 ligases of the cullin 3 family involved in keratin cycling and degradation. Hemidesmosomes have an inner and outer plaque and at least five known constituents. The inner plaque consists of dystonin and plectin, whereas the outer plaque components integrin α6β4 and type XVII collagen traverse the keratinocyte plasma membrane to extend into the lamina lucida. CD151, a transmembrane tetraspanin, closely associates with integrin α6β4 close to the surface of the cell membrane. An electron-dense sub-basal dense plate can sometimes be identified on electron microscopy beneath the hemidesmosome, situated on the outer surface of the cell membrane. Laminins are glycoproteins composed of α, β and γ chains that bind to integrins in the lamina lucida and lamina densa. Laminin 332 is the major component of lamina lucida anchoring filaments, binding integrin α6β4 and integrin α3β1. Inferiorly, anchoring fibrils comprised of laterally aggregated type VII collagen dimers form loops that extend from interactions with type IV collagen within the lamina densa, or extend into the sublamina densa region to interface with electron-dense type IV collagen anchoring plaques. Type VII collagen further interacts with laminins and integrins, and embeds within the dermal extracellular matrix whilst displaying affinity for fibrillary types I and III collagen. Type VII collagen is secreted by keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts as a procollagen molecule comprising a large globular amino-terminal end, a central triple helical rod section (collagenous domain) and a smaller carboxy-terminal end; the triple helix self-assembles into antiparallel dimers, via disulfide bonding in the C-terminal ends, with procollagen C proteinase cleavage causing dimers to aggregate into anchoring fibrils that form the inferior component of the cutaneous basement membrane zone adhesion complex. Kindlin 1 is a focal adhesion protein that contributes to integrin activation through binding of integrin-β tails. Desmosomes are intercellular junctions, comprising transmembrane and intracellular plaque proteins, the main function of which is cell–cell adhesion, although these structures are also involved in signalling and differentiation. Three main protein groups are described: cadherins, comprising desmogleins 1–4 and desmocollins 1–3; armadillo proteins, plakogloblin and plakophilins 1–3; and the plakin protein desmoplakin. EB, epidermolysis bullosa.