![]() More components for
expanding CNebulaX (current release is 1.7.5)
More components for
expanding CNebulaX (current release is 1.7.5)
(1)
Add more deep sky
object databases: more than one million deep sky objects and 25 million stars
(2)
Update the EXE file
with the newest compiled one (correct errors and extent capabilities)
IMPORTANT: The
new databases are only compatible with the current release, CNebulaX,
and further versions
You should
replace old versions (Windex and SkyIndex) with the
new one before expanding the databases
![]() For expanding CNEBULAX:
new databases (latest compiled EXE file below)
For expanding CNEBULAX:
new databases (latest compiled EXE file below)
After the installation of the program, you
will likely wish to expand it by including additional databases. Once installed
them properly in the directories indicated below, the program will show more
that a 1,250,00 deep sky objects, double and variable
stars, plus 25 million stars and 330,000 asteroids and comets. Bellow you will
see the links for downloading the currently available databases. These links
lead to the latest available versions: I will include new updates as I correct
the databases or include new objects (the dates are indicated as a reference).
If you update the database, be sure to be using the latest CNebulaX
exe file (you can update it within this webpage, see below)
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]\GENERAL
Download the GENERAL database
(September 24th, 2007)
The GENERAL database
includes the brightest deep sky objects, double, variable and reference stars.
It represents basically the information shown by CNebulaX
at wide magnifications, and gathers the best deep sky objects in the whole sky,
mainly from the SAC72 database, FK5, and a selection of the Washington Double
Stars and GCVS. This is the standard database distributed with the CNebulaX setup. However, the version included here corrects
some database errors and it is highly recommended. It gathers 32,193 objects.
IMPORTANT:
critical database: please, update it (September 24th, 2007)
(2) Additional non-stellar objects database
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]\NONSTEL
Download the NONSTEL database
(September 1, 2006)
This database expands
the GENERAL database by adding other catalogues: the visual open cluster
catalogue, galaxy clusters (Abell, Zwicky and Hickson), the Strasbourgh-ESO catalogue of planetary nebulae, full NGC
and IC, quasars and radiosources (3C, 4C and others),
and additional bright and dark nebula catalogues (Sh2, LBN, LDN and others). It
gathers 65,987 deep sky objects of very different
nature.
(3) Paturel's
Principal Galaxy Catalogue
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]\GALXY
Download the GALXY database
(September 1, 2006)
The GENERAL database
includes around 7,000 galaxies. The purpose of the GALXY database is to confer CNebulaX a high detail level for zoomed areas. So the GALXY
database gathers the full PGC catalogue: 73,190
galaxies,
which makes navigating by galaxy fields really delicious. I have extended this
number to one million galaxies, with the compilation of the HyperLEDA
database (see below). Nevertheless, the PGC includes more information for each
galaxy, so it is recommended to install it together with HyperLEDA.
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]\DBLST
Download the current DBLST
database (September 24th, 2007)
The GENERAL database
includes just a selection of the best double stars. I have prepared an updated
database, with 106,000 double stars (WDS, February 2005
release). The linked version here is "in progress" (still
unofficial). The USNO team is still working on it in a process that is lasting
several years. So you can enjoy of that new release, still unofficial, but
remarkably more accurate than the current, official one. Do not forget replace
also the GENERAL database.
IMPORTANT:
magnitude/distance code re-calculated: please, update it (September 24th, 2007)
(5) Variable stars: GCVS database
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]\VARST
Download the current VARST
database (September 1, 2006)
I have
included another database: the General Catalogue of Variable stars (GCVS): the
Combined General Catalog of Variable Stars (GCVS 4.2, 2004 Ed.), with 38,624 confirmed variable stars in the main
catalogue, 26,017 suspected
variable stars (NSV catalogue), and around 11,000
stars in external galaxies and supernovae. It is the most extensive, accurate
and recent version. With this new release, the unpleasant position
discrepancies in the old release have become minimal. Do not forget replace
also the GENERAL database.
(6) Still more galaxies? Get the HYPERLEDA: one
million galaxies in your PC !!!!
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]\GALXY
Download the HLEDA database (March
1, 2006)
Do you want the most
powerful catalogue of galaxies? I have prepared an extraordinary, last
addition, more huge and precise than the PGC: the new HyperLEDA catalogue with 983,261
galaxies.
Have a look to the screenshots section
(cluster core view). This is a 30 Mb file, but it is well worth.
(7) An extended star database: the Guide Star Catalogue, 25 million
stars and star-like objects in your PC !!!!
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]
Download the GSC 1.2 database (March
1, 2006)
I have got web space
in the university server, so I have finally linked it. Grab it! It is a huge
120 Mb file, absolutely essential, with more than 25
million stars from GSC 1.2. With it, CNebulaX will get a dramatically new dimension, with a
power enough to face the most difficult deep sky objects you can dream. It is
also essential to overlay CCD images, to identify the contained deep sky
objects. I am planning a still more powerful database: the USNO database, with a
thousand million stars.
(8) New comets and asteroids databases and VSOP87 theory for
planets
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]\Ephem
Comets and brief asteroids databases: Download
Comets and main asteroids (July 30, 2007)
I have placed updates of
the shorter databases installed with the full setup. Since they are not
included in the setup already, maybe you want grab them and update thus
asteroids and comets with the latest databases. The databases from the link
above include 2,388 comets and 13,250 asteroids.
Full asteroids databases: Download full
Asteroids databases #1 and #2 (July 30, 2007)
The ZIP includes two
supplementary asteroids databases. Dabase #1 includes 134,344
"numbered" asteroids, that is, with a known orbit and reliable
predictions. Dabase #2 includes 206,299"unnumbered"
asteroids
(less observed and with a less reliable orbit). These databases are in ASCII
format and with a decoding header for allowing being easily updated or
replaced. The data come from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
IMPORTANT - these DBs require a major update and the EXE
1.05.68 or further.
(9) Moon and Pluto files
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]\Ephem
Download
Moon file (April 2, 2007)
Download
Pluto file (April 1, 2007)
IMPORTANT - this DB requires the EXE 1.06.02 or
further.
Ephemeredes for Pluto
are reliable (topocentric values). The Moon, however,
still is not fully correct: the application of topocentrical
corrections is still partial, although the geocentric position is highly
accurate (1 arcsec). See development
notes. The standard setup installs the full VSOP87 theory for main planets, with
accuracy in the apparent geocentric equatorial coordinates higher than 0.05
arc-seconds, and two other JPL databases for comets and asteroids.
(10) Outlines for deep sky objects: bright and dark nebulae,
supernova remnants, Magellanic clouds,
star clouds, etc
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]\Outlines
Download
Outlines file (September 1, 2006)
IMPORTANT - this DB requires the EXE 1.06.02 or
further.
This is a cooperation
done with Mark Smedley, from Southafrica, who has done a
excellent work. Thanks, Mark!!! See development notes.
(11) Milky Way and Constellation boundaries
(1)
Basic outlines – one
light level prepared
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]
Download
Milky Way profile and constellation boundaries (September 1, 2006)
IMPORTANT - this DB requires the EXE 1.06.02 or
further.
(2)
Extended outlines – five light levels, prepared by Mark Smedley
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]
Download
the extended Milky Way profile (September 24th, 2007)
IMPORTANT - this DB requires the EXE 1.07.01 or
further.
Constellation boundaries
are plotted below 40º zooms. Milky way outlines is
again a cooperation done with Mark Smedley. Again, thanks in the name of all CNebulaX
users. See development notes.
(12) Orbital elements for visual binary stars
Unzip
the files within [RootCNebulaXfolder]\Ephem
Download
the definitive file with orbital elements of ca 2000 double stars
(September 4, 2006)
IMPORTANT - this DB requires the EXE 1.06.04 or
further.
I replaced the
provisional DB with the latest release, with an excellent accuracy in RA and
DEC In addition, I finished some features, so now Visual Binaries feature can
be fully used. See development notes.
WARNING - Please note that these files are only
valid for CNebulaX. Former versions of the
software, called "Windex" (1.01 and 1.02 rs.)
and "SkyIndex" (1.03 rs.)
use a database format different to that of CNebulaX
(1.04 rs and further), and are superseded by CNebulaX (first final version).
Replace the CNebulaX
EXE file by the newest compiled one
![]() The final release could still include small
bugs and some features can be enhanced of finished. My intention is that these modifications
mainly affect the exe file, so you could update your program easily by just
overwriting the old CNebulaX.exe file from the standard installation by the
newest compiled. However, major updates may be required from time to time, and
the EXE works replacing the EXE in the current full installation.
The final release could still include small
bugs and some features can be enhanced of finished. My intention is that these modifications
mainly affect the exe file, so you could update your program easily by just
overwriting the old CNebulaX.exe file from the standard installation by the
newest compiled. However, major updates may be required from time to time, and
the EXE works replacing the EXE in the current full installation.
|
CUMULATIVE UPDATE 1.07.05 (2008/1/7) It only includes
minimal databases and should be updated with the
additional databases in this page This setup will update your setup
replacing old files |
Latest compiled EXE 1.07.05 (2008/1/7) It only includes the latest compiled EXE Compressed ZIP file with the latest EXE Be sure you have a complete
installation: there are other critical files only included in
the full setup file (left) |
Please, report me any problem, doubt
or suggestion. Also, have a look to the FAQ section,
where some common questions are answered.
Note that updating by EXE
overwriting is only possible for CNebulaX: it is not
compatible with former releases, and requires
installing additional files, besides the EXE update
2008-
January - 7 (1.07.05
EXE)
● Deep sky objects are now filled with semitransparent colors The
transparency is increased when the symbol size has been enlarged up to certain level,
to prevent that colors disturb us once the object symbol is too large.
● Help slides have been checked by Casey Skelton, who has made a comprehensive revision. In a
few time the revised HTML documentation will be linked as well, again thanks to
the kind cooperation of Casey Skelton, from Noblesville,
USA.
● Comets and asteroids are loaded in the startup, so that these
objects are shown as the program is loaded.
● Evolution explorer follows the active comet or minor planet
(left click) There is a better coordination of the evolution explorer to make
the forecasting of these bodies easier. Left-click on the comet symbol and then
the explore button to see how it will evolve. Edition of H and G is also
straightforward, and date of the highest brightness within the two years
monitoring period is also given.
● Extended searches: searches in the JUMP combo box are extended
now to comets, asteroids, named stars, common objects, etc. You can now even type partially names of ant kind of objects: "Baxend" (for Baxendell's
nebula), Betelg (for Betelgeuse) (and press ENTER, as
usually)
● Double stars are labeled by default with the name
● As usually, small bugs
and minor issues have been fixed.
2007-
October - 2 (1.07.02
EXE) some small corrections
A new checkbox for forcing monochrome
printouts placed in the print dialog. Explore button now centers the selected
comet/asteroid in the main map before opening the explore window. A bug that
prevented saving accessories list has been fixed.
2007-
September - 24 (1.07.01
EXE) New printing system, orbits explorer, quick slide-show help, orbits
calculation extended to hyperbolic and quasi-parabolic cases, etc
 (1) Printing system
yielding charts similar to the TriAtlas, using a more customizable
interface that can be deployed from either the printer icon (Main/View tab) or the print button in the Edit tab. The quality of printouts,
once particularized the settings to your printer, is excellent. Use the Edit
tab to specify if you want to print color maps: the printer icon apply the
settings in the EDIT tab. The star size, magnitude etc in the Edit tab now
affect specifically to clipboard transferences, since the new interface include
its own controls.
(1) Printing system
yielding charts similar to the TriAtlas, using a more customizable
interface that can be deployed from either the printer icon (Main/View tab) or the print button in the Edit tab. The quality of printouts,
once particularized the settings to your printer, is excellent. Use the Edit
tab to specify if you want to print color maps: the printer icon apply the
settings in the EDIT tab. The star size, magnitude etc in the Edit tab now
affect specifically to clipboard transferences, since the new interface include
its own controls.
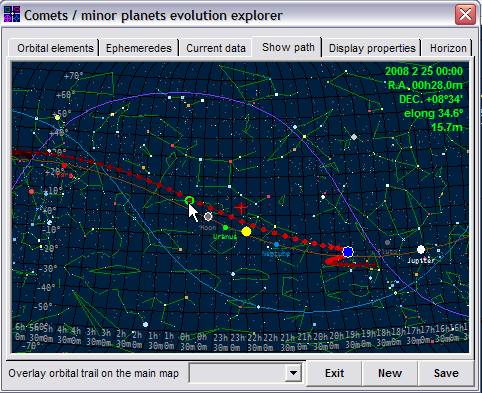
(2) new feature
– Comet
/ Minor Planets EVOLUTION EXPLORER. The Solar System tab has been quite altered. A
Mag button for showing the asteroids and comets lists, sorted by
increasing magnitude, has been added. This is very helpful to locate the
brightest comets and asteroids. There is also another new button, called Explorer, which opens a special window. Note that this is a new
feature, still incipient. The Explorer allows:
2.1. editing orbital elements,
testing (press ENTER to apply), and saving them. H and G parameters can be
easily altered to recalculate the brightness, which to a certain extent
decreases the lack of this data in the JPL comet database. The default H and G
values have been altered to pessimistic figures to get more representative
generic predictions.
2.2. listing some quick
ephemeredes throughout a year
2.3. displaying detailed data of the
comet or asteroid at a given instant
2.4. plotting a special map which
combines the body magnitude and its position, together with Sun evolution as we
move the mouse through the map (see figure)
2.5. monitoring the evolution of five
physical main properties (old "trace"
button)
2.6. plot special horizon maps
at the beginning and the end of the astronomical twilight and midnight, which
in combination with the other features helps to determine the real difficulty
of the observations. Explored dates can be transferred between all these tabs,
so it is quite easy explore what would do a comet or an asteroid throughout a
long time period.
(3) new feature
– All kind of orbits are now included (elliptical, quasi-parabolic, parabolic and hyperbolic
orbits).
In former CNebulaX versions, orbits were processed
only as parabolic or elliptical cases, which was valid for most interesting
comets. However, recent comets with hyperbolic orbits were incorrectly placed
in the sky. Even more important: a serious bug was found (and corrected) in the algorithm for parabolic orbits. Results have been
contrasted with other software including difficult cases of comets in orbit nature
and special time instants.
I think that with all
these changes the predicting system is highly
reliable and very useful to explore comets and asteroids. The way of operating
comets, asteroids and planets is now much better and
easy to work with, especially in what refer to trails. The trace button has
been eliminated.
(4) new feature New Milky Way
multilevel isolines set: A very good
contribution prepared by Mark Smedley. This set includes five light levels to represent the
Milky Way and it is used in conjunction with the old file, still kept for
horizon views. The Milky Way isolines are gradually
shown to avoid slowdown excessively the chart plotting. The new file can be
downloaded from the complements section above, and should be decompressed and
placed in the [RootCnebulaXFolder].
(5) new feature
–
Ephemeredes maker. Feature still incipient. The idea is develop custom tables on
astronomical ephemeredes that will be combined with the maps. At the moment it
is implemented only some basic calculations. This feature will be considerably
enlarged in next updates.,
(6) RA and DEC labels are plotted in the frame, except in polar
views.
In addition, coordinate labels are placed surrounding all the borders, and not
only two of them.
(7) Double stars: The catalogues have been reprocessed to
reassign the double magnitude/distance code (e.g., 2C, 1D), since some errors
have been detected (download the corrected GENERAL and DBLST databases). Stars whose faint component is below the
map threshold although the main one is above it are now plotted as a circle
with two small side segments and no label (to avoid overcrowding), in the same
way as Sky Atlas 2000. Double stars with incomplete information are plotted
similarly.
(8) new feature
– QUICK
VISUAL HELP: To help new users (and perhaps old users too), I have included a
slide show, which is displayed when the program starts (temporarily). This
small presentation calls the attention on some critical points and allows
opening the HTML handbook if the user wants to have a more complete help. I
hope to include more slides in future updates. I think that most new users will
find this information quite helpful to get a better performance of this
software. The HTML handbook has been updated to release 1.7.1.
(9) Modified searches in the Quick Finder: if after pressing
ENTER to locate any string in the Quick Finder lists, no coincidence is found, the
search is extended to the external databases as if the search was typed in the
JUMP combo box.
(10) Default observing list includes Herschel 400, Dyer and
Messier objects, highlighted in the main map. However, Southern Sky
bright objects are still poorly represented. I need to find a reliable
selection of the best southern objects (suggestions are welcome) and mix it
with the current one. I find quite convenient having this great selection of
bright objects marked and available to display data, maps, and pictures in the
observing list viewer. The marker size has been reduced (see the picture
below).
(11) Full sky view in horizontal coordinates has been included
in the Quick Finder upper tabs (FS tab). The default zooms are
now 120, 40, 10, 4 and 1º (customizable, as before),
(12) Some small but important bugs solved. One of them had serious consequences on parabolic orbits.
Other affected the calculation of rise, transit and sets of moving
objects.
2007-
July-30 (1.06.15
EXE) Some minor bugs corrected
Some minor changes
done, but nothing still relevant.
2006-
September-22 (1.06.09
EXE) Some minor bugs corrected
Earth-view plots are now (default option)
periodically updated, with a frequency of one re-plot by minute. Some bugs in
the "Night info" facility have been corrected. Please, report me any
bug you could detect. There are too many changes, and testing is required to
fix small problems.
2006-September-4
Faster plots. Visual binaries database corrected
(1) Solar System ephemeredes are updated at a custom rate (default,
2 minutes). This way, one of the most restrictive factors delaying the plots
has been removed and the program is now much faster, which allows rebuilding
maps more often (panning, repeated zooms, use of cursor keys, etc)
(2) Visual binaries New catalogue
replacing the provisional one has been uploaded. It is also contained in the
1.06.04 update, also uploaded.
2006-September-1
Updated standard setup files. EXE 1.06.02 available and cumulative update
1.06.02 available to download
(1) More than 200 nebulae outlines done in cooperation
with Mark Smedley, from Southafrica. There in 207 files for bright & dark
nebulae, supernova remnants, the Magellanic Clouds
and some star clouds.
(2) A local horizon editor: mountains, hills, etc, can be now
overlaid. Several local horizons can be stored and loaded.
(3) Finally, Earth view maps integrated in the main maps. To
activate it, just zoom out to a value >150º to switch on it, or click the
new tabs at the upper right toolbox (N, E, S, W). In horizontal mode the
custom local horizon is also overlaid,
(4) Observing list can be deployed including special maps and
photos.
There is an all-sky view and horizontal, ecliptic and galactic views. Also, a
feature that I like a lot: a gradual-zoom finding system, with several
predefined zooms in consecutive tabs.
(5) Default observing list ("program.obs"
file) is autoloaded and displayed in the main map and in the new horizon views.
(6) Visual binaries (orbital double stars) are now available, although I am not
satisfied with the catalogue (poor accuracy in RA/DEC values); I will replace
it soon.
(7) Ephemeredes for Pluto and the Moon. The topocentric accuracy for Pluto is highly satisfactory. For
the Moon, the geocentric accuracy is of 1 arcsec, but
the topocentrical corrections still are not correct,
although local situation of the observer is considered.
(8) A tab with a list of the last visited objects to return to them
quickly is situated within the Main tab
(9) The Milky Way is plotted as outlines
(10) The ecliptic is plotted with Sun tips indicating the
situation throughout the year
(12) The galactic equator is plotted with longitude tips
(13) The horizon is plotted with azimuth tips
(14) Constellation
boundaries are plotted below a certain magnification
(15) There are now 6 customizable tabs to set user's zoom
levels and N, E, W and S
Earth-views. Now horizontal maps are easy to switch and very handy.
(16) Cluttering has been
decreased:
more adaptive rules on the DSO shown, and last shown
stars are points, except at high magnifications.
(17) A time picker allows plot the sky at
certain instants (twilights, midnight, moon/sun set, rise and transit, etc)
Numerous
corrections have been included attending all reports I have received up to
the moment, plus all the bugs that I located in the summer testing. Update the associated new files (9-12) to use the new
release, or install the new full setup file. Please, report me any problem or
doubt. Take into account the high number of changes: testing is needed to fix bugs.
2006-June-29
Updated standard setup files. EXE 1.05.75 available and cumulative update
1.05.75 available to download
For a couple of days I have had problems in the setup.
The update is finally ready. Sorry for the inconveniences.
new - Bright
/ Dark Nebulae outlines - The program now can overlay nebulae profiles. I have
only included 25 large winter nebulae and the veil nebulae. My intention is to
add more in next updates. The new files are included in the EXE update (it is
not necessary reinstalling).
new - Constellation
boundaries - Finally, the constellation limits are plotted in the main map.
A new default color combination is required to avoid cluttering (go to the
Setup/Colors tab and change to the default colors.
new - Milky
Way outline - Just a first draft, but this feature will be enhanced soon. At
the moment, at least the Milky Way can be barely seen.
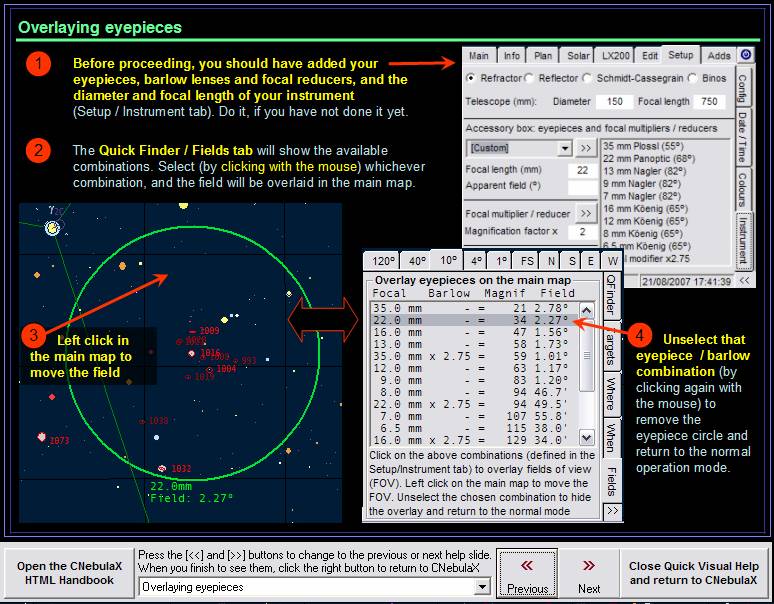
new - Eyepiece
editor and new eyepiece overlay system - The eyepiece classes are stored now with
apparent fields and the combination of eyepiece and focal reducer/extender are
chosen from a list in the Quick Finder. Activating any item in the list overlay
the eyepiece field, that can be moved with the mouse.
2006-June-6
Updated standard setup files. EXE 1.05.71 available
new - Cumulative
update (1.05.71) has been placed in the website - This exe implements
all corrections found, related to some failures in the jump combo box and
ephemeredes. The DSO finder is by default shown in the startup to help
beginners (fold it with the lower [<<] label).
(1) Some Latitude and Longitude settings
problems have been corrected. Date and time can be changed now graphically from
the Day, Month and Year plots and from the "where" tab. Comets and
asteroids are plotted with an auxiliary trail informing of the position
occupied 24 hours before. Comets are now plotted wit a core surrounded by
activity circles indicating likely CO2 and H2O activity
(distance <2.5 and <1.5 AU from the Sun, respectively)
(2) Digital Settings Circles mode - It is in beta
testing step, with major improvements still to be done. If you have digital
setting circles, install an LX200 emulator and you can use CNebulaX
for monitoring telescope position. It is still unfinished and scarcely tested,
but it is useable (report me problems and suggestions).
2006-May-22
1.05.68 EXE file
Minor update (1.05.68) - Deployable toolbox
with a more finished deep sky objects finder interface, heading to the final
interface. The toolbox is now deployable in two nested levels (DSO finder and
notebook), accessible from the [>>] symbol at the lower right corner.
(1) The first level displays the DSO and
constellations finder (center+frame), some lists of
objects lists (Messier+Dyer, Herschel'400, deep sky
objects with common names, and stars by common name), and a locator at 5 zoom
levels with a tabbed interface (the "where...?" tab)
(2) The second level of deployment is only available
at 1024x768 or higher screen resolutions, and by now it give
access to the notebook. It includes a new screen mode that docks the main map
in a landscape view, quite good for telescope control,
like you can see below. I like this screen mode, it is
very comfortable with the finder and the annotation facility at hand.
2006-May-14:
1.05.65 EXE, it requires major update 1.05.59
new - Minor
update (1.05.65) - Fast deep sky objects finder: two interlinked lists
(constellations and object class), that can be used to see the deep sky objects
fulfilling the selection. If you have linked images to CNebulaX,
single clicking on the found DSOs will show a picture in the viewer and some
extra data. Double click on the list will center the map in the selected object,
and will set it as the active one.
Finished more corrections to solar system
objects - CNebulaX
now displays topocentric apparent equatorial
coordinates, with an error smaller than 0.05 arc seconds. Minor bodies and
comets are now also corrected by the local situation of the observer on the
Earth. High accuracy for Moon still is not included, and Pluto is not
implemented yet. Satellite ephemeredes are on the way.
2006-May-7
new - New
setup files (1.05.61) - in English, a self-containing all the auxiliary files in
the standard of Visual Studio Windows Installer (MSI files).
new - Major
update (1.05.59) - it requires reinstalling the program
(overwrite the old installation) - It includes solar system, asteroids and
minor planets ephemeredes, including plotting orbital trails. A lot of other
changes have been implemented. Some of them are: (1) a new secondary tab series
for Solar System ephemeredes, (2) plotting observation lists in the main map,
(3) a new notebook area, (4) a jump combo box for quick access to some lists
(Herschel 400, Messier, bright stars, best double stars, etc), (5) printing
improvements, (6) an expanded handbook, (7) moving the toolbox, (8) saving the INIs, notes, notebook and observation lists in a supervised
way, and (9) faster start-up and running.
under development - More work on ephemeredes.
2006-April-9
new - print-out
facility finally finished, update your EXE file!!!!
There was bug hard to trap: (1) failures were apparently unpredictable, (2) I
have had to repeat a lot of printings up to catch it, and (3) simple maps were often well printed but complex maps usually failed. It is now fixed, and
finally the program is able to print excellent colour or monochrome maps, customisable
from the EDIT tab. If you want to have a look to the print-outs, I have copied
here a PDF showing the M13 area generated with CNebulaX. I am fully satisfied. There is a preview/draft
facility that passes a B/W map to the clipboard as well. There are some other
minor bugs fixed, one of them affecting the behaviour of the undocked viewer.
under development - an ephemerid system and databases for calculating and plotting minor
planets and comets. The updated exe includes new calculation facilities but
they are still inactivated. Be a little patient, it is on the way...
2006-March-23
new - overlay external tables (up to develop an ephemerids
system); more convenient display of the observation program (list mode) from
the Main/Viewer; it now loads the default observation program from the Help
icon; new combo box for changing the viewer mode
stars in color - Updated
Tycho II database
with spectral information has been loaded in the website. The new source is Kharchenko revision, including its extensions. It is
compressed in the standard CNebulaX setup file, so to
get the new file: (1) download and uncompress the setup zip file, (2)
open the cabinet file "CNebulaX.CAB" using winzip or similar, (3) extract CONSTEL.DAT, (4) replace the
old CONSTEL.DAT in your old installation with the new one, and (5) replace
CNebulaX.exe with the updated exe
file
corrections - syncronisation between navigator and main
map; faster loading; small bugs in the viewer corrected.
2006-March-1
new - Implements
access to the new database HyperLEDA. It also
includes modified code to show stars in color according to its spectra. Updated
Tycho II database still not loaded in the website.