Highlights
Towards the development of highly sensitive opto-mechanical sensors
The development of point sensors based on stimulated forward Brillouin scattering (SFBS) using conventional optical fibers will benefit from our recent results. On the one hand, we investigated in detail how the length of the fiber section, its diameter and the mass attached to the surface determine the signal to noise ratio and the frequency shift of the acoustic resonances. In particular, we paid attention to the operation of the sensor as an all-optical mass microbalance (Optics Express 32, 100114, 2024). On the other hand, we continue working on developing new alternatives for the implementation of efficient probe techniques (Journal of Lightwave Technology 2025).
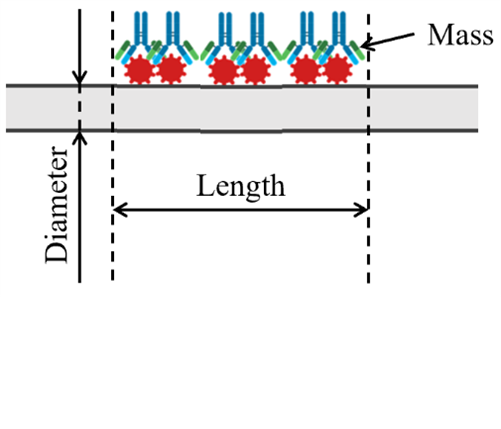
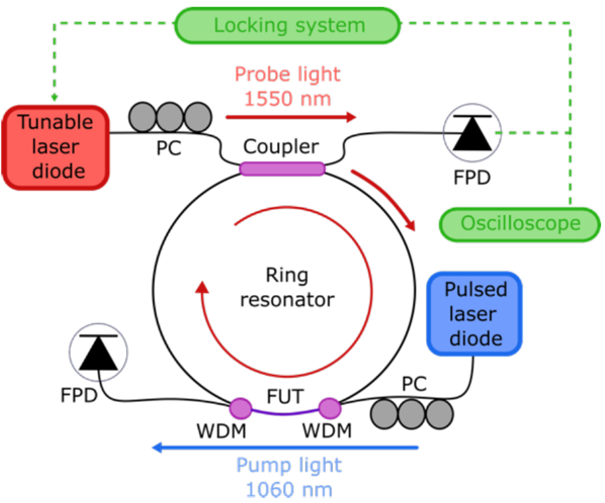
Proposal of point biosensor based on SFBS (left) and new probe technique based on a resonant fiber ring (right).
Multifrequency nonlinear Schrodinger equation
Making traditionally forbidden regimes possible, nonlinearity dispersion management is offering a growing number of promising opportunities. However, standard methods in nonlinear fiber optics were conceived for fibers which nonlinearities hardly depended on wavelength. Consequently, such approaches could now hinder the development of this research avenue. Over recent years, we released the typical nonlinearity measurement from its demand for low dispersion (see highlights below). Now we have rigorously derived a theory accounting for the multifrequency nature of the nonlinear coefficient dispersion with the computational advantages that the conventional model reached renouncing the photon number conservation. As such, this tool can be instrumental to unveil the potential that dispersive nonlinearities hold (Optics Letters 49, pp. 4713, 2024).
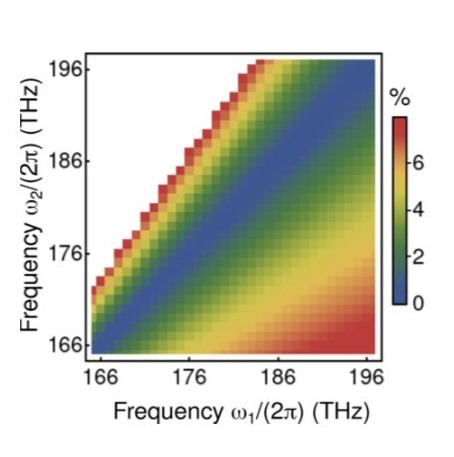
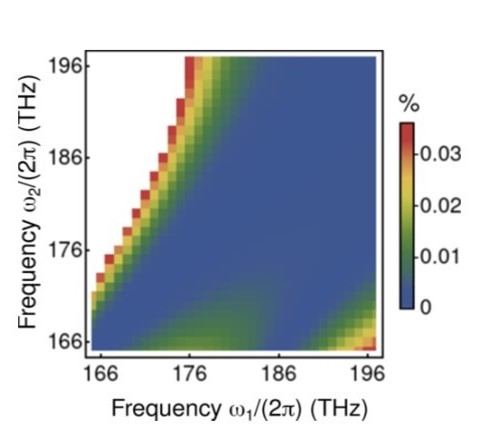
For the LP02 mode of a step-index fiber of 13 μm diameter and 0.2 numerical aperture and the processes 2ω1 → ω2 + [ω = ω1 − (ω2 − ω1)]︁, relative error of the nonlinear coefficient corresponding to (left) the conventional model and (right) our new multifrequency nonlinear Schrödinger equation.
Forward Brillouin scattering spectroscopy in optical fibers with whispering-gallery modes (WGM)
Transverse acoustic mode resonances (TAMRs) in optical fibers –which generate forward Brillouin scattering– are being promoted as the physical mechanism for new fiber-sensing concepts. The interplay between TAMRs and WGM resonances in standard optical fibers can be exploited for probing the opto-excited TAMRs using the WGM resonances. This novel probing technique provides the narrowest linewidths ever reported for the TAMRs, and demonstrates an optimum efficiency for the detection of low order TAMRs.
(Advanced Optical Materials, 2301629, 2023).
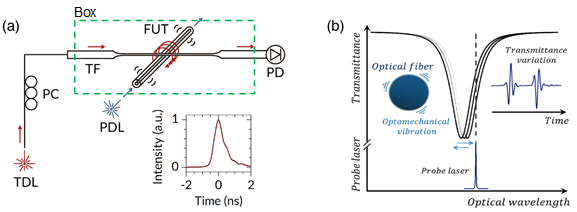
(a) Experimental setup for excitation of WGM resonances of FUT and the acoustic resonance with the PDL. TDL: tunable diode laser; PC: polarization controller; PDL: pulsed diode laser; PD: photodiode; OSC: oscilloscope; TF: tapered fiber. Inset shows the temporal profile of the pump pulses.
(b) Schematic illustration of the probing method: the transmittance of probe laser is modulated by the acoustic resonances of the FUT.
Measurement of the nonlinear coefficient accounting for dispersion and loss
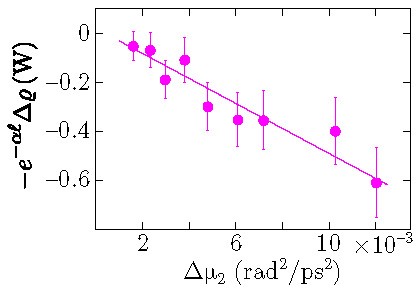
A balance law of the generalized nonlinear Schrödinger equation (GNLSE) allows removing fundamental limitations on the measurement accuracy of the nonlinear coefficient γ due to chromatic dispersion β2 and loss α. In our method, changes on the intensity autocorrelation at zero time delay ρ and the root-mean-square spectral width μ2 at different powers are measured, and processed by means of the propagation equation for ρ and μ2 recently derived from the GNLSE. Using this approach, we have successfully measured γ in a kilometer-long standard fiber pumped close to 2 μm, where α is more than 50 times larger than at 1.55 μm (Optics Letters 48, 493-496, 2023).
This paper has been the fifth most downloaded of its journal in its publication month.
Recent advances in Forward Brillouin Scattering (FBS): Sensor applications
Point sensors based on FBS using the pump & probe technique developed in our laboratory have demonstrated to have a high potential for the development of new sensor applications. Our technique provides good signal to noise ratio (SNR) and the narrowest linewidths reported to date. FBS enables sensing the surrounding of the optical fiber in a similar way to the optical evanescent field sensors, but using the acoustic field. This review discusses the characteristics of the proposed point sensors and their potential for new sensor concepts (Sensors 23, 318, 2023)
This article in Sensors is included in the list of Most Notable Articles (November 2022–January 2023).
The principle of operation of the sensor can be compared to the operation of a bell, one feeds it and it resonates with a characteristic frequency and damping that contains the sensor information. If the sensor is operated as a frequency codified sensor, then its robustness and high accuracy read-out can be assured.
Simultaneous measurement of temperature and strain using a single point sensor.
Accurate determination of Poisson’s ratio in optical fibers, and strain and
temperature measurement discrimination using Forward Brillouin Scattering (FBS)
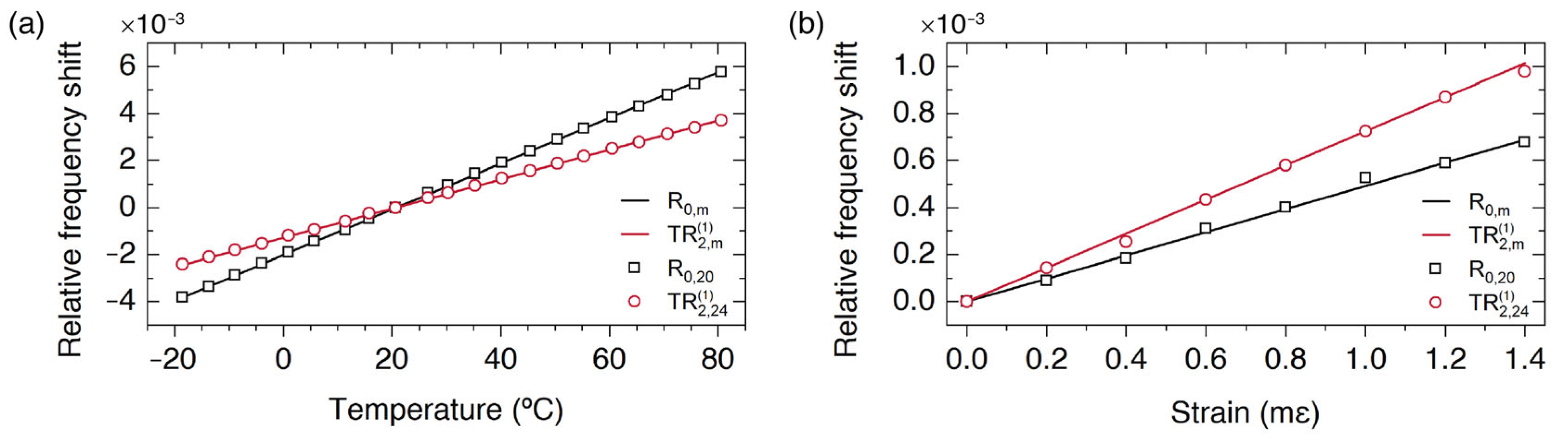
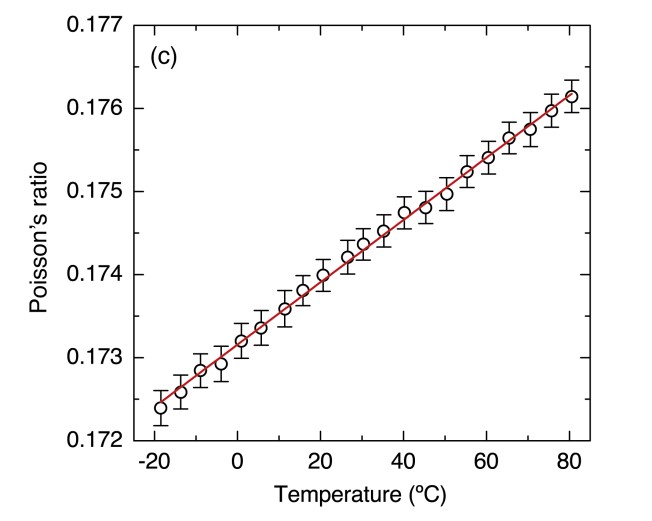
FSBS enables a high accuracy measurement of Poisson’s ratio (ν) of optical fibers and its temperature dependence (Opt. Express 30, 42-52, 2022). Our approach is based on an all-optical pump and probe technique used for the excitation and characterization of both, radial and torsional-radial acoustic resonances of optical fibers (Opt. Lett. 45, 5331-5334, 2020). This technique enables simultaneous measurement of strain and temperature using a single point sensor (Opt. Express. 30, 14384-14392, 2022). Following this approach, the determination of Poisson’s ratio does not require the measurement of any physical length, but only frequency measurements. The dependence of fiber Poisson’s ratio with temperature is also determined experimentally.
This article in Optics Express has been highlighted as an Editor's Pick.

Record accuracy measurement of phase and group refractive indices of optical fibers
Weak fiber Bragg gratings enable high accuracy measurement of the absolute modal refraction index of the fundamental mode in single-mode fibers. We also demonstrate a new method to measure the group index, and report on the thermo-optic and the strain-optic coefficients as a function of the wavelength (Appl. Opt. 60, 2824-2832, 2021. Several standard optical fibers were characterized: Corning SMF28 telecom fiber, Fibercore HB1250 polarization maintaining fiber and Fibecore M5 erbium doped fiber. *Aplied Optics' Editors have chosen this paper to be highlighted as an Editor's Pick.*
Novel concept for in-fiber biosensors: Bio-Bragg Gratings
We present the design, fabrication, and proof of concept of a novel biosensor based on a bio-Bragg-grating (BBG) that is imprinted on the surface of a microfiber. Our approach combines the ability to pattern a periodic network of bioreceptors on the surface of a microfiber, with the sensing capacity of microfibers due to its enhanced evanescent optical field. The bioreceptors (BSA, in our case) are placed in a periodic fashion onto the fiber surface by microcontact printing. The interaction between the fundamental optical mode of the microfiber and this incipient BBG leads to a weak reflection peak in the optical response of the device.
The biosensing transduction principle relies on the fact that, if the specific target (IgGs in this case) is present in the external medium, it will bind to the bioreceptors that conform the BBG, increasing its reflectivity. As a result, it will be possible to quantify the concentration of specific IgGs by measuring such reflectivity. Tunability of the BBG response, wavelength multiplexation, and minimized non-specific binding signal contributions are demonstrated.
This work has been published in Biosensors and Bioelectronics (Biosensors & Bioelectronics, Vol. 176, art. 112916, (2021)), and was registered as a national patent (ES2749689 / G01N21/17).
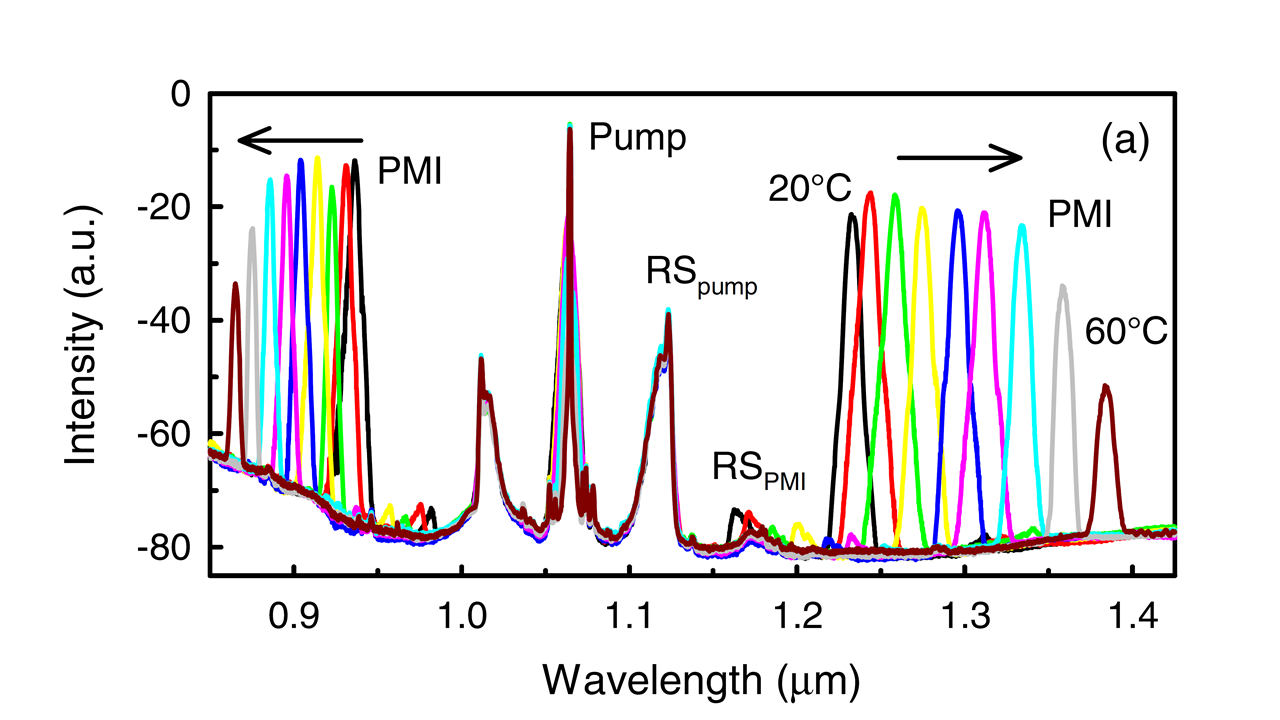
Broadband tuning of polarization modulation (PMI) in photonic crystal fibers (PCF)
Wideband tuning of strong bands generated through polarization modulation instability (PMI) in photonic crystal fibers (PCF) is achieved via thermal tuning of fiber’s chromatic dispersion and birefringence, using PCFs infiltrated with ethanol and pumped at 1064 nm (Optics Letters 45, 4891-4894, 2020). In a previous article, we demonstrated tunable PMI in all-normal dispersion (AND-i) photonic crystal fibers, in which scalar four wave mixing (FWM) was forbidden (IEEE Photonics Journal 11, art. 7104108, 2019).
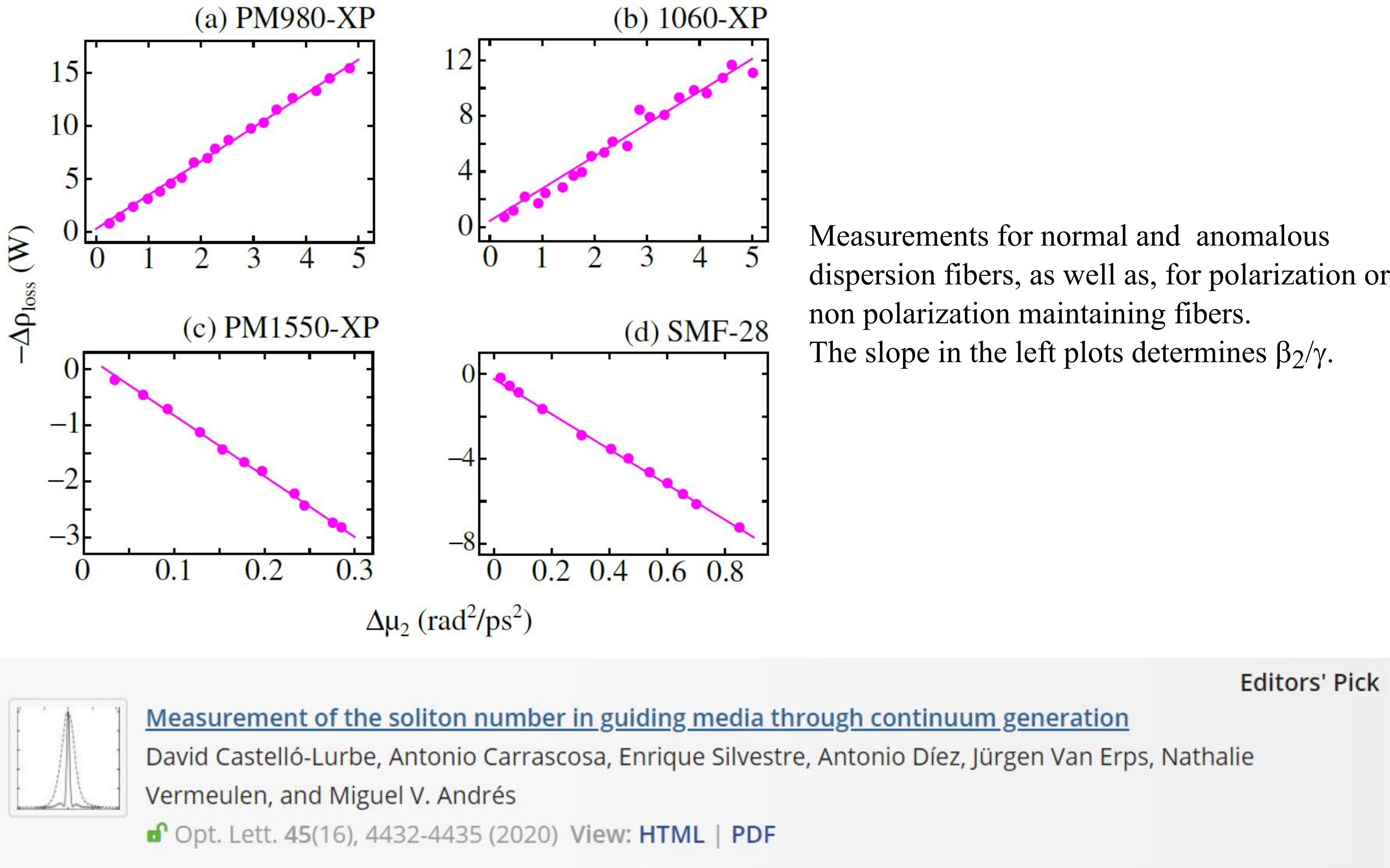
Direct measurement of the ratio between chromatic dispersion and the nonlinear coefficient
The fundamentals of our measuring method is based on a conservation law of the nonlinear Schrödinger equation, so it is not limited to specific ranges of chromatic dispersion and nonlinear coefficient values, in contrast to previous approaches. Measuring the increments of intensity autocorrelation at zero time delay (which provides -Δρloss), and the square of the rms spectral width (Δμ2) at different powers, for a given fiber length, one obtains directly the ratio between chromatic dispersion and the nonlinear coefficient (β2/γ). (Optics Letters 45, 4432-4435, 2020) *Optics Letters' Editors have chosen this paper to be highlighted as an Editor's Pick.*
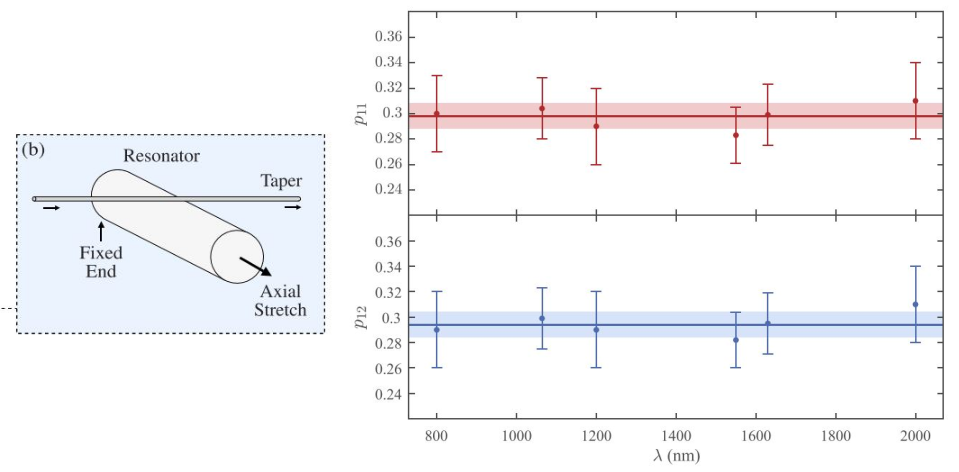
Measurement of the strain-optic coefficients of PMMA from 800 to 2000 nm
PMMA Pockels' coefficients exhibit negligible dispersion and anisotropy in the wavelength range [800, 2000] nm:
p11 = 0.298 ± 0.010 p12 = 0.294 ± 0.010
The strain-optic coefficients were measured using a technique based on the excitation of azimuthal whispering gallery modes resonances in thin PMMA cylinders (OSA Continuum 3, 441-446, 2020). The technique was previously demonstrated using silica fibers (Optics Letters 41, 2934-2937, 2016).
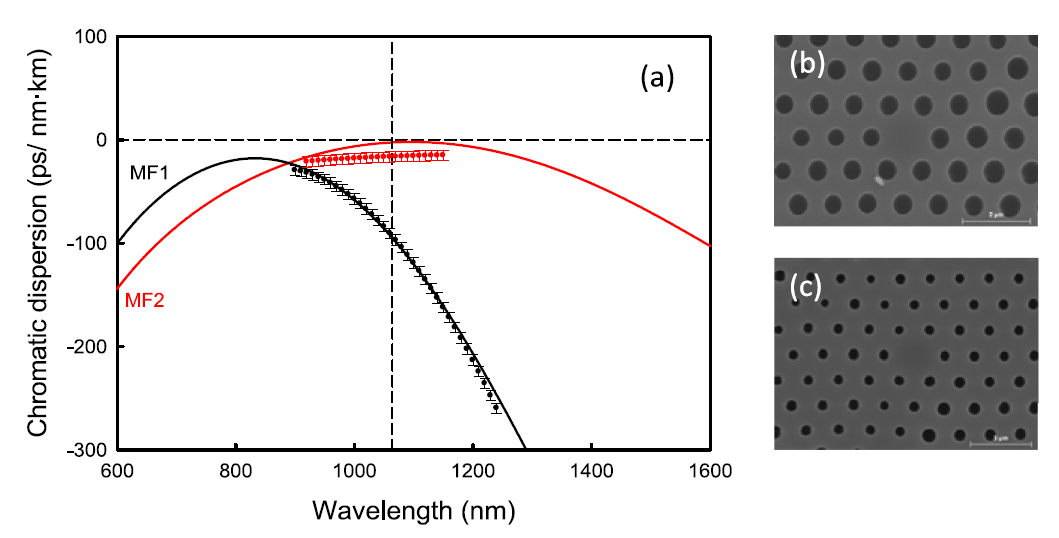
Polarization modulation instability (PMI) in all-normal dispersion (ANDi) photonic crystal fibers (PCF)
PMI enables a controlled generation of new frequencies in ANDi fibers, in which scalar four wave mixing (FWM) is forbidden. Several ANDi - PCF were designed and fabricated at the LFO facilities. A detailed experimental and theoretical characterization of PMI in these ANDi - PCF was carried out (IEEE Photonics Journal 11, art. 7104108, 2019). This work is part of a project focused on the development of new tunable light sources based on FWM in nonlinear PCF with special dispersion properties.
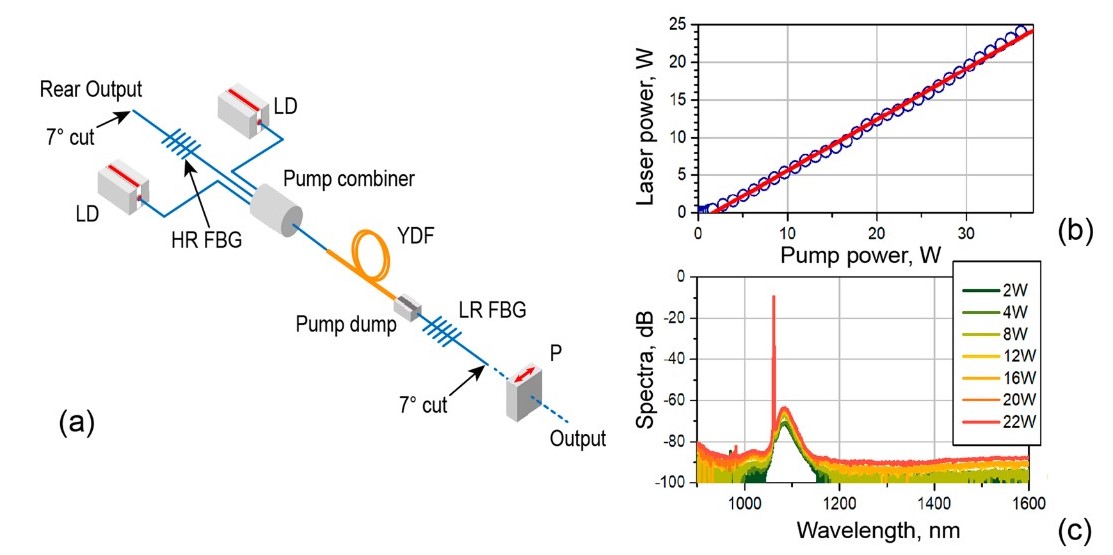
20 W Yb fiber laser: random noise pulsed regime
We show that the laser output obeys the photon statistics inherent to narrowband amplified spontaneous emission and that the noise pulsing is properly addressed in terms of probability density and autocorrelation functions. Our novel approach reveals, in particular, that the regime’s coherence time dramatically shortens, from few ns to tens ps, with increasing laser power (Scientific Reports 9, art. 13073, 2019)
Special Fiber Gratings
Recent advances in fiber grating fabrication: (Left) Single-mode Bragg gratings in tapered few-mode and multimode fibers (Optics Letters 44, 4024-4027, 2019), and (Right) long period gratings with subnanometric linewidths (Optics Letters 42, 1265-1268, 2017). These fabrication improvements have pushed forward some applications in photonic fractional signal processing (Progress in Optics 63, 93-178, 2018).

