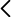Effect of Choline Chloride-Based DES on the Pore-Forming Ability and Properties of PVDF Membranes Prepared with Triethyl Phosphate as Green Solvent
- Autors: Alejando Gálvez-Subiela, Ramón Jiménez-Robles, José David Badia, Marta Izquierdo, Amparo Chafer. (2025).
- Tipus de publicació: Article
- Titol publicació (nom del llibre o de la revista): Polymers (Basel). Num.17(7), 984.
-
Resum:
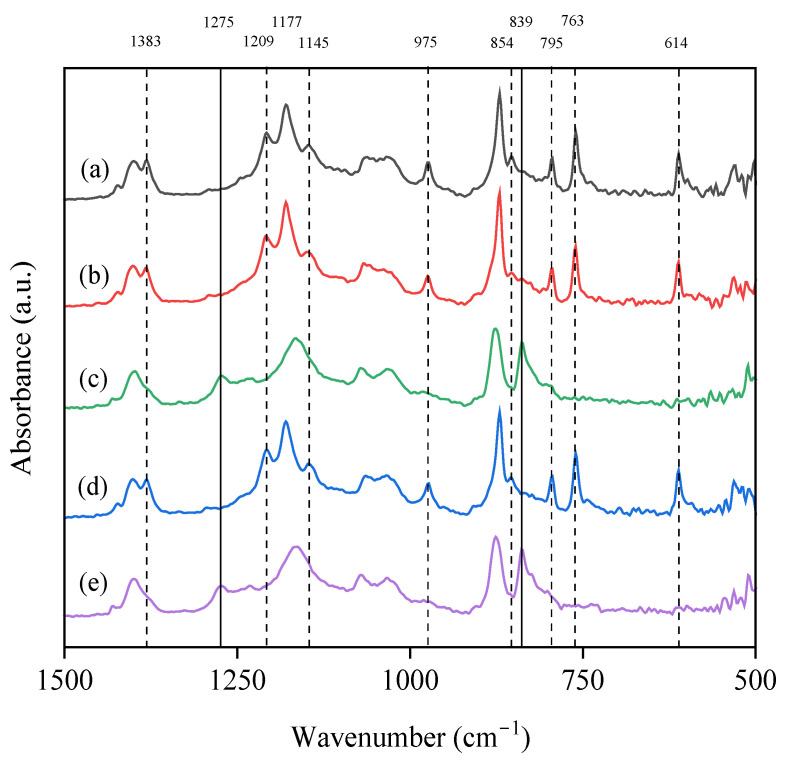
Superhydrophobic poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes were obtained by a surface treatment consisting of oxygen plasma activation followed by functionalisation with a mixture of silica precursor (SiP) (tetraethyl-orthosilicate [TEOS] or 3-(triethoxysilyl)-propylamine [APTES]) and a fluoroalkylsilane (1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctyltriethoxysilane), and were benchmarked with coated membranes without plasma activation. The modifications acted mainly on the suThis study explores the influence of various additives on the morphological, chemical, and thermal properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes prepared via the non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS) technique. The use of a green solvent such as triethyl phosphate (TEP) was shown to be successful. A particular focus was dedicated to pore formers based on choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents (DES) in combination with ethylene glycol and glycerol, i.e., ChCl/EG and ChCl/GLY, and its benchmark with traditional counterparts such as poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and glycerol (GLY). Comprehensive characterization was conducted using FESEM, FTIR, XRD, and DSC techniques to evaluate changes in membrane morphology, porosity, and crystallinity. PEG acted as a pore-forming agent, transitioning the internal structure from spherulitic to sponge-like with consistent pore sizes, while GLY produced a nodular morphology at higher concentrations due to increased dope solution viscosity. DES induced significant shifts in crystalline phase composition, decreasing α-phase fractions and promoting β-phase formation at higher concentrations. While the overall porosity remained unaffected by the addition of GLY or PEG, it was dependent on the DES concentration in the dope at lower values than those obtained by GLY and PEG. Membrane pore size with ChCl/GLY was lower than with ChCl/EG and GLY. All membranes showed performance at the hydrophobic regime. The findings demonstrate that ChCl/EG and ChCl/GLY can tailor the structural and thermal properties of TEP-driven PVDF membranes, providing a green and versatile approach to customize the membrane properties for specific applications.
Keywords: choline chloride; deep eutectic solvent (DES); glycerol; green solvent; membrane; non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS); poly(vinylidene fluoride) PVDF; polyethylene glycol (PEG); triethyl phosphate (TEP).
Gálvez-Subiela, A., Jiménez-Robles, R., Badia-Valiente, J. D., Izquierdo, M., & Chafer, A. (2025). Effect of Choline Chloride-Based DES on the Pore-Forming Ability and Properties of PVDF Membranes Prepared with Triethyl Phosphate as Green Solvent. Polymers, 17(7), 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070984
DOI: 10.3390/polym17070984