CO2 AND AIR CIRCULATION
To reduce the risk of aerosol transmission of pathogens in indoor environments, it is effective to improve air circulation. Air circulation is understood as the renewal of indoor air with outdoor air. There are different methods to determine whether a space is poorly ventilated. One of them is the measurement of the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere.
CO2 is present in the air under normal conditions, with a certain concentration. In a closed room, its concentration increases as a result of people’s breathing and decreases with the ventilation of the room. Therefore, the measured value of its concentration in parts per million (ppm) represents an indicator of good and bad ventilation of the space occupied by people and is an aid in deciding what action to take.
Ideally, natural cross ventilation should be provided by opening opposing doors and windows, and if this is not possible, mechanical air circulation without recirculation.
How to manage air circulation from the CO2 data obtained?
With this algorithm we are able to decide the actions to be carried out depending on the CO2 results:
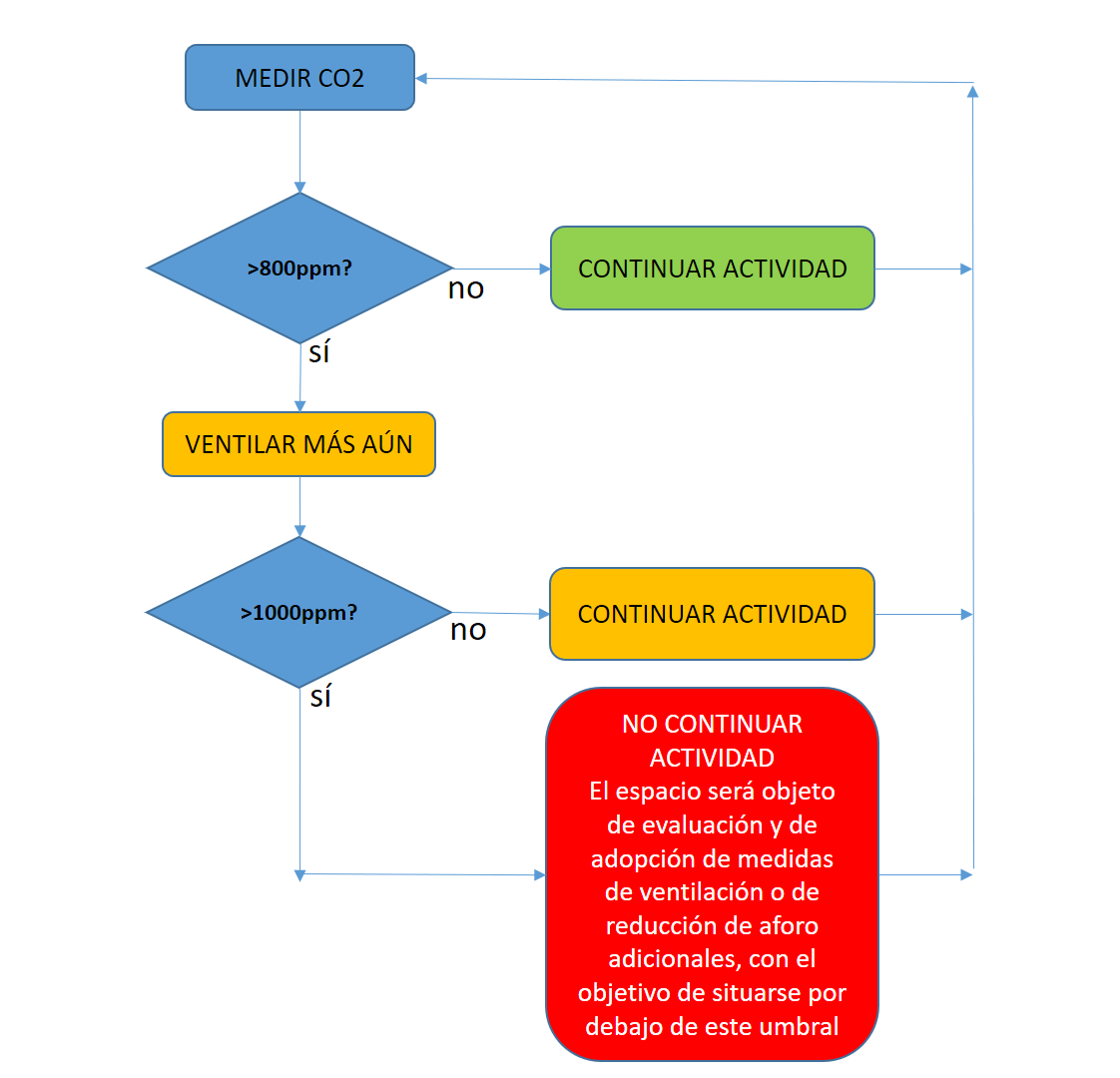
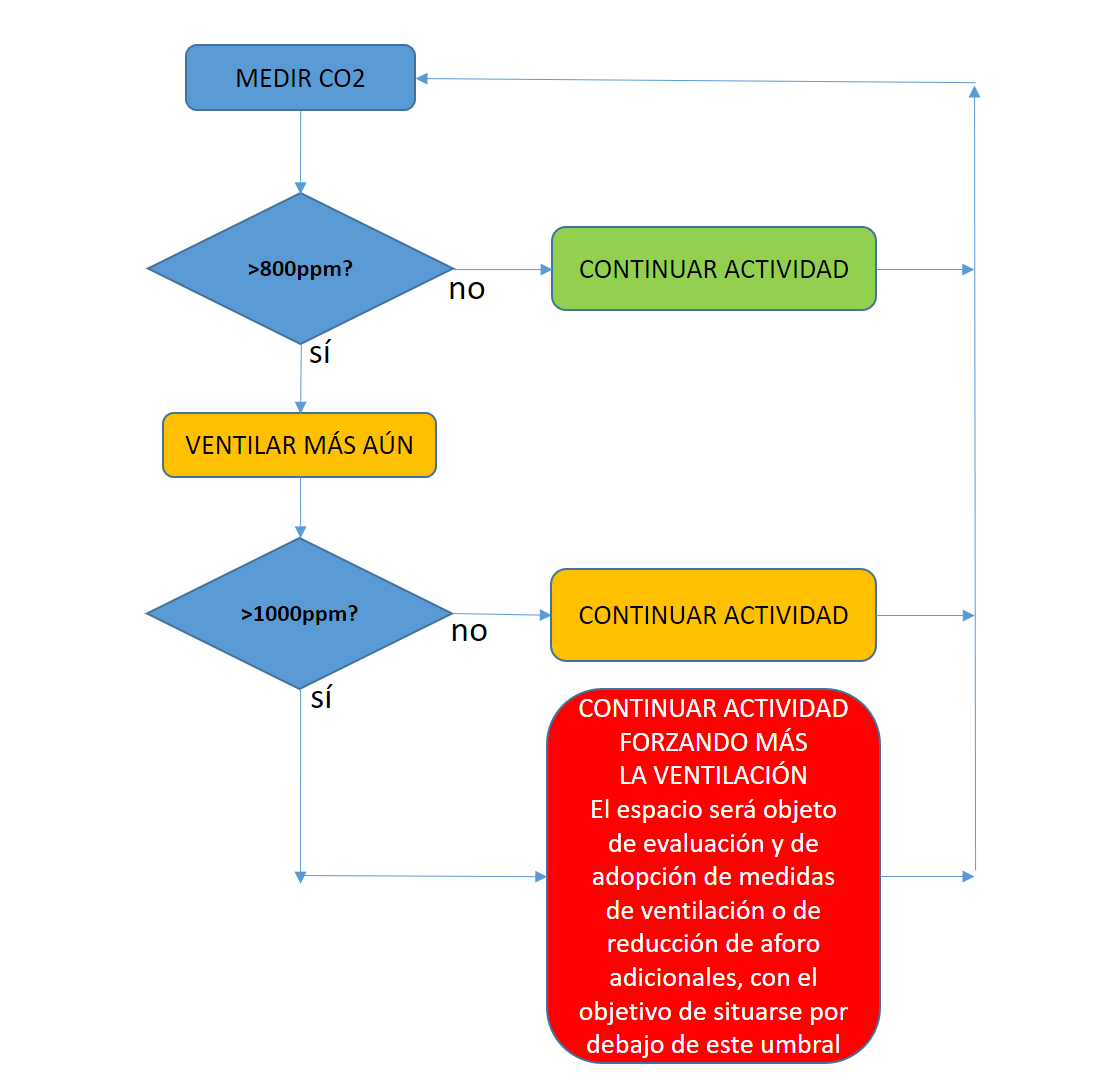
Finally, we remind you that CO2 measurement complements (not replaces) the rest of the universally known measures against COVID-19.






