 English Español Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
English Español Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
 English Español Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
English Español Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
Facultat de Ciències Biològiques

LABORATORY: EXTRACELULAR MATRIX PROTEINS: adhesion & cell signaling.Study on the in vivo interaction between integrins and fibronectin by knockin mice.
Fibronectin is an ubiquitous and abundant protein in extracellular matrices (ECM) that binds other ECM proteins (like collagen, fibrin, proteoglycans and fibronectin itself) and cell adhesion molecules (integrins and syndecans)controlling adhesion, migration, proliferation and cell survival. The alternative splicing of the unique FN gen generates several isoforms. In tissues, the cells secrete FN in its soluble dimeric form. Subsequently this dimers will assemble forming a multimeric fibrli complex around cell surfaces. However, in blood plasma we can find abundant FN on its soluble form.
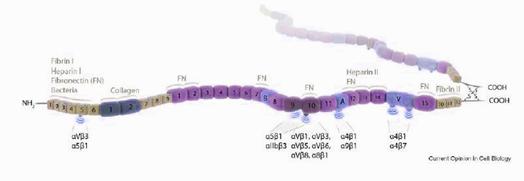
Numerous in vitro and cell culture experiments have demostrated the important role of some fibronectin regions to bind integrins. Knockout-FN mice have early embryonic lethality, and exhibit several mesoderm defects. Also, the deletion of the major integrins that bind FN, such as α5 and α4, produce complex phenotypes with rather early embryonic lethality,making impossible to explain the specific role of fibronectin-integrins interactions during development.
In our lab, we are establishing different mice strains (knock-in) that express integrin-binding deficient FNs, and analyzing the functional consequences during development and the inmune system.
We are focus in the following specific mutant mice and interactions:
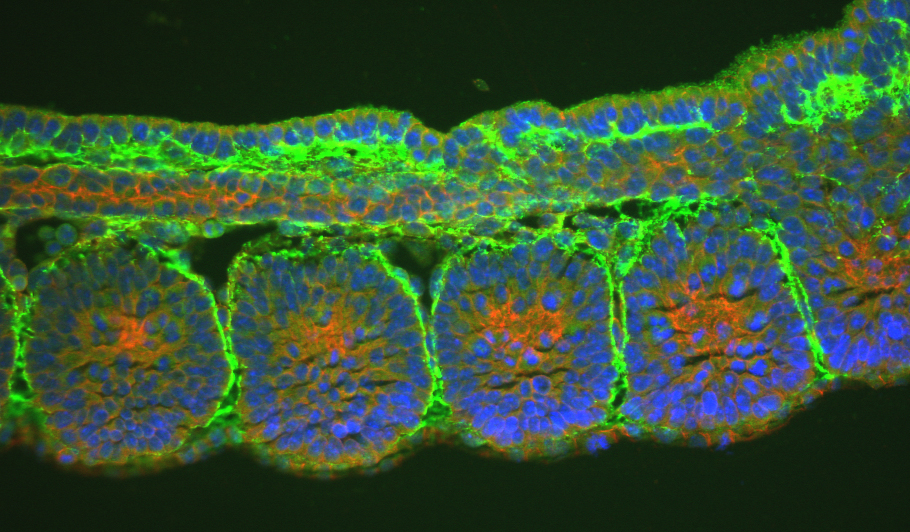
1) mice where the RGD motif (FNIII10) has been changed by RGE. This substitution abolishes the interaction between FN-RGD and α5β1 or αvβ3 integrins in vivo. The main phenotypic features of the mutant are: defectives angiogenesis and somitogenesis.
2) mice expressing a mutated variable region of FN (FN-IIICS). This modification abolishes FN binding to α4β1 and α4β7integrins. Haematopoiesis, angiogenesis and leukocyte extravasatian towards inflamation sites are the expected altered functions in these mice.
3) mice expressing a mutated synergy site (FNIII9) which cooperates in the interaction between the RGD domain and integrins. We expect defects related with the integrin activated function.
Presentation go -> Main research points go-> Fibronectin go-> Perlecan go-> Members go-> Publications go-> PhD go->
Laboratorio IX
2ºPlanta Edificio AFacultat de Ciències Biològiques
Universitat de València
Dr. Moliner, 50
46100 Burjassot, València
Phone: 96 3543796/963543020
Fax: 96 354 43 72
e-mail: Mercedes.Costell@uv.es