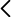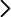
Conferències al DAA. Xarrada a càrrec de l'investigador Matteo Bugli, del CEA Saclay - IRFU/DAp, França. Lloc: Seminari del Departament d'Astronomia i Astrofísica, 4a planta de l'Edifici d'Investigació, a Burjassot. Dia: divendres 1 de juny de 2018. Hora: 12:00.
RESUM:
Geometrically thick tori have been widely used in the last decades to model accretion flows onto black holes. They are prone to develop a number of different instabilities, but the most important is certainly the magnetorotational instability (MRI), which triggers transport of angular momentum outwards on dynamical time-scales and the onset of MHD turbulence.
However, hydrodynamic tori are also known to be unstable to the so-called Papaloizou-Pringle instability (PPI), which leads to the growth of large-scale non-axisymmetric modes that could in principle produce a detectable gravitational wave signal.
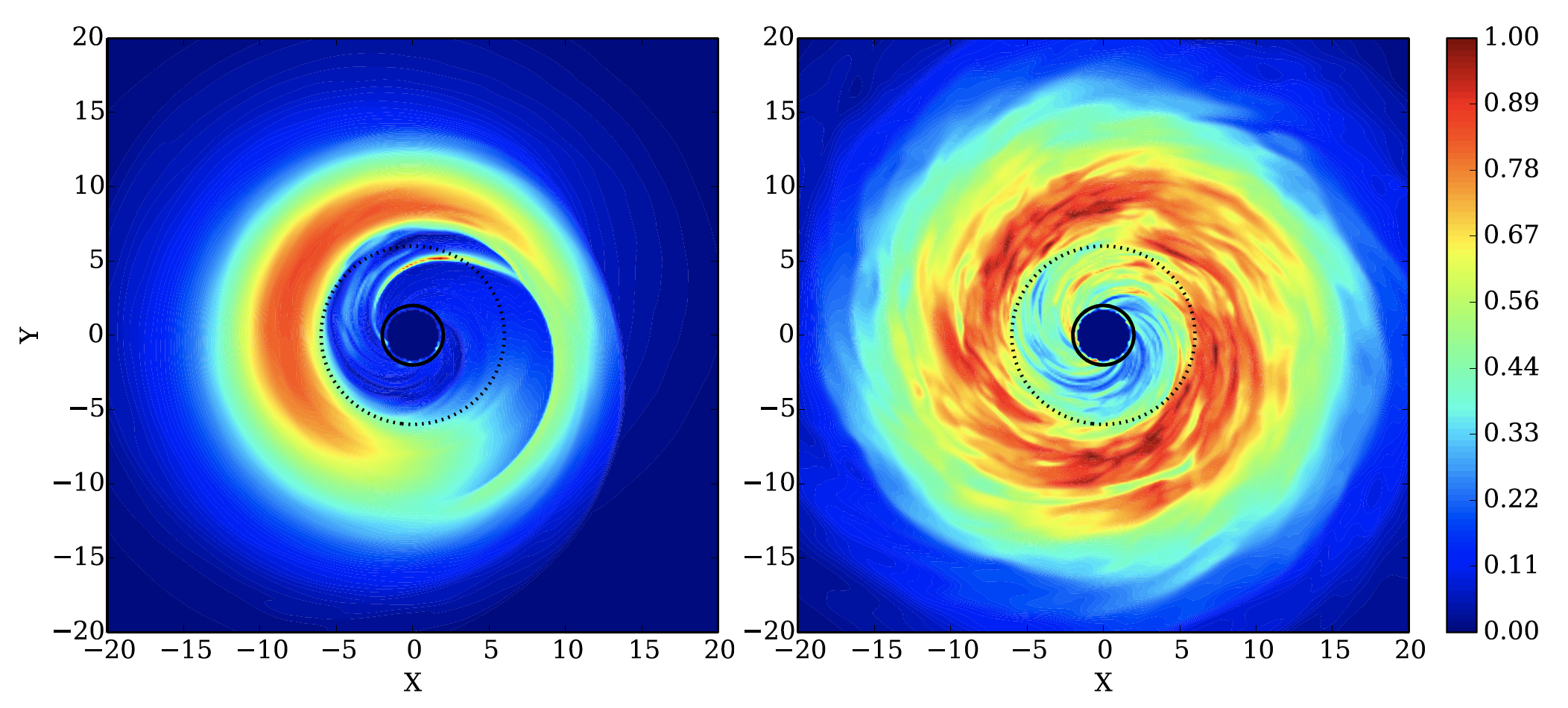
Using 3D GRMHD simulations, we investigated the competition between these two instabilities considering a range of different magnetic field strengths and spectra of the initial perturbations, verifying how the action of non-axisymmetric MRI effectively suppresses the growth of the m=1 azimuthal mode selected by the PPI (although a transient growth of large-scale modes may still occur).
However, relaxing the ideal MHD approximation and introducing the effects of a turbulent resistivity can inhibit the onset of the MHD turbulence, hence allowing for a significant development of the hydrodynamic instability.