-
Yeast Translation Elongation Factor eIF5A Expression Is Regulated by Nutrient Availability through Different Signalling Pathways
Barba-Aliaga M, Villarroel-Vicente C, Stanciu A, Corman A, Martínez-Pastor MT, Alepuz P*
(2020). ArticleInternational Journal of Molecular Sciences. No.2020 Dec 28;22(1):219
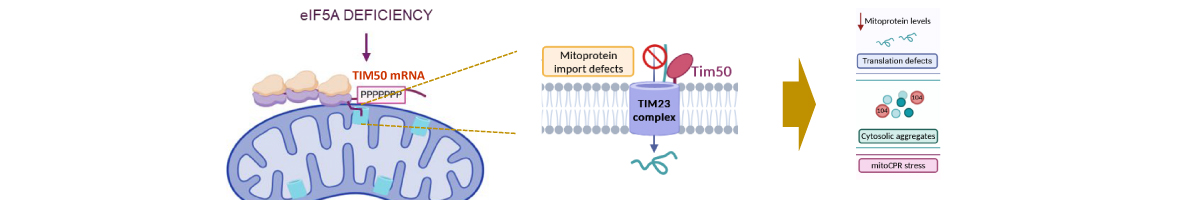
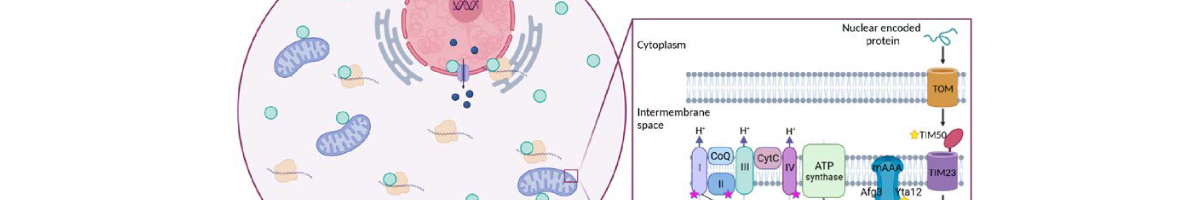
Translation elongation factor eIF5A binds to ribosomes to promote peptide bonds between problematic amino acids for the reaction like prolines. eIF5A is highly conserved and essential in eukaryotes, which usually contain two similar but differentially expressed paralogue genes. The human eIF5A-1 isoform is abundant and implicated in some cancer types; the eIF5A-2 isoform is absent in most cells but becomes overexpressed in many metastatic cancers. Several reports have connected eIF5A and mitochondria because it co-purifies with the organelle or its inhibition reduces respiration and mitochondrial enzyme levels. However, the mechanisms of eIF5A mitochondrial function, and whether eIF5A...
Translation elongation factor eIF5A binds to ribosomes to promote peptide bonds between problematic amino acids for the reaction like prolines. eIF5A is highly conserved and essential in eukaryotes, which usually contain two similar but differentially expressed paralogue genes. The human eIF5A-1 isoform is abundant and implicated in some cancer types; the eIF5A-2 isoform is absent in most cells but becomes overexpressed in many metastatic cancers. Several reports have connected eIF5A and mitochondria because it co-purifies with the organelle or its inhibition reduces respiration and mitochondrial enzyme levels. However, the mechanisms of eIF5A mitochondrial function, and whether eIF5A expression is regulated by the mitochondrial metabolism, are unknown. We analysed the expression of yeast eIF5A isoforms Tif51A and Tif51B under several metabolic conditions and in mutants. The depletion of Tif51A, but not Tif51B, compromised yeast growth under respiration and reduced oxygen consumption. Tif51A expression followed dual positive regulation: by high glucose through TORC1 signalling, like other translation factors, to promote growth and by low glucose or non-fermentative carbon sources through Snf1 and heme-dependent transcription factor Hap1 to promote respiration. Upon iron depletion, Tif51A was down-regulated and Tif51B up-regulated. Both were Hap1-dependent. Our results demonstrate eIF5A expression regulation by cellular metabolic status.
Read more HidePMID: 33379337
*corresponding author
DOI: 10.3390/ijms22010219 -
Recruitment of Xrn1 to stress-induced genes allows efficient transcription by controlling RNA polymerase II backtracking
García-Martínez J, Pérez-Martínez ME, Pérez-Ortín JE, Alepuz P*.
(2020). ArticleRNA Biology. No.Volume 18, 2021 - Issue 10 (p.1458-1474)
A new paradigm has emerged proposing that the crosstalk between nuclear transcription and cytoplasmic mRNA stability keeps robust mRNA levels in cells under steady-state conditions. A key piece in this crosstalk is the highly conserved 5′–3′ RNA exonuclease Xrn1, which degrades most cytoplasmic mRNAs but also associates with nuclear chromatin to activate transcription by not well-understood mechanisms. Here, we investigated the role of Xrn1 in the transcriptional response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells to osmotic stress. We show that a lack of Xrn1 results in much lower transcriptional induction of the upregulated genes but in similar high levels of their transcripts because of parallel...
A new paradigm has emerged proposing that the crosstalk between nuclear transcription and cytoplasmic mRNA stability keeps robust mRNA levels in cells under steady-state conditions. A key piece in this crosstalk is the highly conserved 5′–3′ RNA exonuclease Xrn1, which degrades most cytoplasmic mRNAs but also associates with nuclear chromatin to activate transcription by not well-understood mechanisms. Here, we investigated the role of Xrn1 in the transcriptional response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells to osmotic stress. We show that a lack of Xrn1 results in much lower transcriptional induction of the upregulated genes but in similar high levels of their transcripts because of parallel mRNA stabilization. Unexpectedly, lower transcription in xrn1 occurs with a higher accumulation of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) at stress-inducible genes, suggesting that this polymerase remains inactive backtracked. Xrn1 seems to be directly implicated in the formation of a competent elongation complex because Xrn1 is recruited to the osmotic stress-upregulated genes in parallel with the RNAPII complex, and both are dependent on the mitogen-activated protein kinase Hog1. Our findings extend the role of Xrn1 in preventing the accumulation of inactive RNAPII at highly induced genes to other situations of rapid and strong transcriptional upregulation.
Read more HidePMID: 33258404
*corresponding author
DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1857521 -

Nut1/Hos1 and Sas2/Rpd3 control the H3 acetylation of two different sets of osmotic stress-induced genes
Pérez-Martínez ME, Benet M, Alepuz P, Tordera V.
(2020). ArticleEpigenetics. No.Mar;15(3):251-271
Epigenetic information is able to interact with the cellular environment and could be especially useful for reprograming gene expression in response to a physiological perturbation. In fact the genes induced or repressed by osmotic stress undergo significant changes in terms of the levels of various histone modifications, especially in the acetylation levels of histone H3. Exposing yeast to high osmolarity results in the activation of stress-activated protein kinase Hog1, which plays a central role in gene expression control. We evaluated the connection between the presence of Hog1 and changes in histone H3 acetylation in stress-regulated genes. We found a parallel increase in the...
Epigenetic information is able to interact with the cellular environment and could be especially useful for reprograming gene expression in response to a physiological perturbation. In fact the genes induced or repressed by osmotic stress undergo significant changes in terms of the levels of various histone modifications, especially in the acetylation levels of histone H3. Exposing yeast to high osmolarity results in the activation of stress-activated protein kinase Hog1, which plays a central role in gene expression control. We evaluated the connection between the presence of Hog1 and changes in histone H3 acetylation in stress-regulated genes. We found a parallel increase in the acetylation of lysines 9 and 14 of H3 in induced genes during stress, which was largely dependent on Hog1 at the genome-wide level. Conversely, we observed that acetylation decreased in repressed genes and was not dependent on Hog1. However, lack of Hog1 sometimes produced different, and even opposite, effects on the induction and acetylation of H3 of each gene. We also found that the acetylation state of lysine 9 of H3 was altered in the strains deficient in Nut1 HAT and Hos1 HDAC in the genes up-regulated during osmotic stress in an Msn2/Msn4-independent manner, while lysine 9 acetylation of H3 varied in the strains deficient in Sas2 HAT and Rpd3 HDAC for the Msn2/Msn4-dependent induced genes. The results presented here show new, unexpected participants in gene regulation processes in response to environmental perturbations.
Read more Hide DOI: 10.1080/15592294.2019.1664229 -
Global translational repression induced by iron deficiency in yeast depends on the Gcn2/eIF2α pathway
Romero AM, Ramos-Alonso L, Alepuz P, Puig S, Martínez-Pastor MT
(2020). ArticleScientific Reports. No.Jan 14;10(1):233
Iron is an essential element for all eukaryotic organisms because it participates as a redox active cofactor in a wide range of biological processes, including protein synthesis. Translation is probably the most energy consuming process in cells. Therefore, one of the initial responses of eukaryotic cells to stress or nutrient limitation is the arrest of mRNA translation. In first instance, the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae responds to iron deficiency by activating iron acquisition and remodeling cellular metabolism in order to prioritize essential over non-essential iron-dependent processes. We have determined that, despite a global decrease in transcription, mRNA translation is...
Iron is an essential element for all eukaryotic organisms because it participates as a redox active cofactor in a wide range of biological processes, including protein synthesis. Translation is probably the most energy consuming process in cells. Therefore, one of the initial responses of eukaryotic cells to stress or nutrient limitation is the arrest of mRNA translation. In first instance, the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae responds to iron deficiency by activating iron acquisition and remodeling cellular metabolism in order to prioritize essential over non-essential iron-dependent processes. We have determined that, despite a global decrease in transcription, mRNA translation is actively maintained during a short-term exposure to iron scarcity. However, a more severe iron deficiency condition induces a global repression of translation. Our results indicate that the Gcn2-eIF2α pathway limits general translation at its initiation step during iron deficiency. This bulk translational inhibition depends on the uncharged tRNA sensing Gcn1-Gcn20 complex. The involvement of the Gcn2-eIF2α pathway in the response to iron deficiency highlights its central role in the eukaryotic response to stress or nutritional deprivation, which is conserved from yeast to mammals.
Read more Hide DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-57132-0 -
RNA-binding proteins as targets to improve salt stress tolerance in crops
Téllez, S.R.; Kanhonou, R.; Bellés, C.C.; Serrano, R.; Alepuz, P.; Ros, R.
(2020). ArticleAgronomy. No.Volume 10, Issue 2
Salt stress drastically reduce crop productivity. In order to identify genes that could improve crop salt tolerance, we randomly expressed a cDNA library of the halotolerant sugar beet in a sodium-sensitive yeast strain. We identified six sugar beet genes coding for RNA binding proteins (RBP) able to increase the yeast Na+-tolerance. Two of these genes, named Beta vulgaris Salt Tolerant 3 (BvSATO3) and BvU2AF35b, participate in RNA splicing. The other four BvSATO genes (BvSATO1, BvSATO2, BvSATO4 and BvSATO6) are putatively involved in other processes of RNA metabolism. BvU2AF35b improved the growth of a wild type yeast strain under salt stress, and also in mutant backgrounds with impaired...
Salt stress drastically reduce crop productivity. In order to identify genes that could improve crop salt tolerance, we randomly expressed a cDNA library of the halotolerant sugar beet in a sodium-sensitive yeast strain. We identified six sugar beet genes coding for RNA binding proteins (RBP) able to increase the yeast Na+-tolerance. Two of these genes, named Beta vulgaris Salt Tolerant 3 (BvSATO3) and BvU2AF35b, participate in RNA splicing. The other four BvSATO genes (BvSATO1, BvSATO2, BvSATO4 and BvSATO6) are putatively involved in other processes of RNA metabolism. BvU2AF35b improved the growth of a wild type yeast strain under salt stress, and also in mutant backgrounds with impaired splicing, thus confirming that splicing is a target of salt toxicity. To validate the yeast approach, we characterized BvSATO1 in sugar beet and Arabidopsis. BvSATO1 expression was repressed by salt treatment in sugar beet, suggesting that this gene could be a target of salt toxicity. Expression of BvSATO1 in Arabidopsis increased the plant salt tolerance. Our results suggest that not only RNA splicing, but RNA metabolic processes such as such as RNA stability or nonsense-mediated mRNA decay may also be affected by salt stress and could be biotechnological targets for crop improvement.
Read more HideKeywords: RNA-binding proteins; salt toxicity; sugar beet; yeast
DOI: 10.3390/agronomy10020250 -
Nut1/Hos1 and Sas2/Rpd3 control the H3 acetylation of two different sets of osmotic stress-induced genes.
Pérez-Martínez ME, Benet M, Alepuz P*, Tordera V*.
(2019). ArticleEpigenics. No.Volume 15, 2020 - Issue 3 (p. 251-271)
Epigenetic information is able to interact with the cellular environment and could be especially useful for reprograming gene expression in response to a physiological perturbation. In fact the genes induced or repressed by osmotic stress undergo significant changes in terms of the levels of various histone modifications, especially in the acetylation levels of histone H3. Exposing yeast to high osmolarity results in the activation of stress-activated protein kinase Hog1, which plays a central role in gene expression control. We evaluated the connection between the presence of Hog1 and changes in histone H3 acetylation in stress-regulated genes. We found a parallel increase in the...
Epigenetic information is able to interact with the cellular environment and could be especially useful for reprograming gene expression in response to a physiological perturbation. In fact the genes induced or repressed by osmotic stress undergo significant changes in terms of the levels of various histone modifications, especially in the acetylation levels of histone H3. Exposing yeast to high osmolarity results in the activation of stress-activated protein kinase Hog1, which plays a central role in gene expression control. We evaluated the connection between the presence of Hog1 and changes in histone H3 acetylation in stress-regulated genes. We found a parallel increase in the acetylation of lysines 9 and 14 of H3 in induced genes during stress, which was largely dependent on Hog1 at the genome-wide level. Conversely, we observed that acetylation decreased in repressed genes and was not dependent on Hog1. However, lack of Hog1 sometimes produced different, and even opposite, effects on the induction and acetylation of H3 of each gene. We also found that the acetylation state of lysine 9 of H3 was altered in the strains deficient in Nut1 HAT and Hos1 HDAC in the genes up-regulated during osmotic stress in an Msn2/Msn4-independent manner, while lysine 9 acetylation of H3 varied in the strains deficient in Sas2 HAT and Rpd3 HDAC for the Msn2/Msn4-dependent induced genes. The results presented here show new, unexpected participants in gene regulation processes in response to environmental perturbations.
Read more HidePMID: 31512982
*corresponding author
DOI: 10.1080/15592294.2019.1664229 -
Karyopherin Msn5 is involved in a novel mechanism controlling the cellular level of cell cycle regulators Cln2 and Swi5
Quilis I, Taberner FJ, Martínez-Garay CA, Alepuz P, Igual JC.
(2019). ArticleCell Cycle. No.Mar;18(5):580-595
The yeast β-karyopherin Msn5 controls the SBF cell-cycle transcription factor, responsible for the periodic expression of CLN2 cyclin gene at G1/S, and the nuclear export of Cln2 protein. Here we show that Msn5 regulates Cln2 by an additional mechanism. Inactivation of Msn5 causes a severe reduction in the cellular content of Cln2. This occurs by a post-transcriptional mechanism, since CLN2 mRNA level is not importantly affected in asynchronous cultures. Cln2 stability is not significantly altered in msn5 cells and inactivation of Msn5 causes a reduction in protein level even when Cln2 is stabilized. Therefore, the reduced amount of Cln2 in msn5 cells is mainly due not to a higher rate of...
The yeast β-karyopherin Msn5 controls the SBF cell-cycle transcription factor, responsible for the periodic expression of CLN2 cyclin gene at G1/S, and the nuclear export of Cln2 protein. Here we show that Msn5 regulates Cln2 by an additional mechanism. Inactivation of Msn5 causes a severe reduction in the cellular content of Cln2. This occurs by a post-transcriptional mechanism, since CLN2 mRNA level is not importantly affected in asynchronous cultures. Cln2 stability is not significantly altered in msn5 cells and inactivation of Msn5 causes a reduction in protein level even when Cln2 is stabilized. Therefore, the reduced amount of Cln2 in msn5 cells is mainly due not to a higher rate of protein degradation but to a defect in Cln2 synthesis. In fact, analysis of polysome profiles indicated that Msn5 inactivation causes a shift of CLN2 and SWI5 mRNAs from heavy-polysomal to light-polysomal and non-polysomal fractions, supporting a defect in Cln2 and Swi5 protein synthesis in the msn5 mutant. The analysis of truncated versions of Cln2 and of chimeric cyclins combining distinct domains from Cln2 and the related Cln1 cyclin identified an internal region in Cln2 from 181 to 225 residues that when fused to GFP is able to confer Msn5-dependent regulation of protein cellular content. Finally, we showed that a high level of Cln2 is toxic in the absence of Msn5. In summary, we described that Msn5 is required for the proper protein synthesis of specific proteins, introducing a new level of control of cell cycle regulators.
Read more Hide DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1578148 -
The Lsm1-7/Pat1 complex binds to stress-activated mRNAs and modulates the response to hyperosmotic shock.
Garre E, Pelechano V, Sánchez Del Pino M, Alepuz P, Sunnerhagen P.
(2018). ArticleRNA-binding proteins (RBPs) establish the cellular fate of a transcript, but an understanding of these processes has been limited by a lack of identified specific interactions between RNA and protein molecules. Using MS2 RNA tagging, we have purified proteins associated with individual mRNA species induced by osmotic stress, STL1 and GPD1. We found members of the Lsm1-7/Pat1 RBP complex to preferentially bind these mRNAs, relative to the non-stress induced mRNAs, HYP2 and ASH1. To assess the functional importance, we mutated components of the Lsm1-7/Pat1 RBP complex and analyzed the impact on expression of osmostress gene products. We observed a defect in global translation inhibition under...
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) establish the cellular fate of a transcript, but an understanding of these processes has been limited by a lack of identified specific interactions between RNA and protein molecules. Using MS2 RNA tagging, we have purified proteins associated with individual mRNA species induced by osmotic stress, STL1 and GPD1. We found members of the Lsm1-7/Pat1 RBP complex to preferentially bind these mRNAs, relative to the non-stress induced mRNAs, HYP2 and ASH1. To assess the functional importance, we mutated components of the Lsm1-7/Pat1 RBP complex and analyzed the impact on expression of osmostress gene products. We observed a defect in global translation inhibition under osmotic stress in pat1 and lsm1 mutants, which correlated with an abnormally high association of both non-stress and stress-induced mRNAs to translationally active polysomes. Additionally, for stress-induced proteins normally triggered only by moderate or high osmostress, in the mutants the protein levels rose high already at weak hyperosmosis. Analysis of ribosome passage on mRNAs through co-translational decay from the 5’ end (5P-Seq) showed increased ribosome accumulation in lsm1 and pat1 mutants upstream of the start codon. This effect was particularly strong for mRNAs induced under osmostress. Thus, our results indicate that, in addition to its role in degradation, the Lsm1-7/Pat1 complex acts as a selective translational repressor, having stronger effect over the translation initiation of heavily expressed mRNAs. Binding of the Lsm1-7/Pat1p complex to osmostress-induced mRNAs mitigates their translation, suppressing it in conditions of weak or no stress, and avoiding a hyperresponse when triggered.
Read more HidePMID: 30059503
*corresponding author
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007563 -
The 5' Untranslated Region of the EFG1 Transcript Promotes Its Translation To Regulate Hyphal Morphogenesis in Candida albicans
Desai PR, Lengeler K, Kapitan M, Janßen SM, Alepuz P, Jacobsen ID, Ernst JF
(2018). ArticlemSphere. No.2018 Jul 5;3(4):e00280-18
Extensive 5′ untranslated regions (UTR) are a hallmark of transcripts determining hyphal morphogenesis in Candida albicans. The major transcripts of the EFG1 gene, which are responsible for cellular morphogenesis and metabolism, contain a 5′ UTR of up to 1,170 nucleotides (nt). Deletion analyses of the 5′ UTR revealed a 218-nt sequence that is required for production of the Efg1 protein and its functions in filamentation, without lowering the level and integrity of the EFG1 transcript. Polysomal analyses revealed that the 218-nt 5′ UTR sequence is required for efficient translation of the Efg1 protein. Replacement of the EFG1 open reading frame (ORF) by the heterologous reporter gene...
Extensive 5′ untranslated regions (UTR) are a hallmark of transcripts determining hyphal morphogenesis in Candida albicans. The major transcripts of the EFG1 gene, which are responsible for cellular morphogenesis and metabolism, contain a 5′ UTR of up to 1,170 nucleotides (nt). Deletion analyses of the 5′ UTR revealed a 218-nt sequence that is required for production of the Efg1 protein and its functions in filamentation, without lowering the level and integrity of the EFG1 transcript. Polysomal analyses revealed that the 218-nt 5′ UTR sequence is required for efficient translation of the Efg1 protein. Replacement of the EFG1 open reading frame (ORF) by the heterologous reporter gene CaCBGluc confirmed the positive regulatory importance of the identified 5′ UTR sequence. In contrast to other reported transcripts containing extensive 5′ UTR sequences, these results indicate the positive translational function of the 5′ UTR sequence in the EFG1 transcript, which is observed in the context of the native EFG1 promoter. It is proposed that the 5′ UTR recruits regulatory factors, possibly during emergence of the native transcript, which aid in translation of the EFG1 transcript.
Read more HideIMPORTANCE Many of the virulence traits that make Candida albicans an important human fungal pathogen are regulated on a transcriptional level. Here, we report an important regulatory contribution of translation, which is exerted by the extensive 5′ untranslated regulatory sequence (5′ UTR) of the transcript for the protein Efg1, which determines growth, metabolism, and filamentation in the fungus. The presence of the 5′ UTR is required for efficient translation of Efg1, to promote filamentation. Because transcripts for many relevant regulators contain extensive 5′ UTR sequences, it appears that the virulence of C. albicans depends on the combination of transcriptional and translational regulatory mechanisms.
[Read more] [Hide] DOI: 10.1128/msphere.00280-18 -
Repositorio Datos: Published Dataset Table 2 and Suppl Table S1
Garre, E., Pelechano, V., Sánchez del Pino, M. Alepuz, P. and Sunnerhagen, P.
(2018). Recurs electrònicPLoS Genet. No.14(7):e1007563
Acceso dataset: Artículo y base datos propia. Tipo de datos: Proteómica