Sewer Mining, Microplastics Removal, Leakage Reduction: REWAISE and the ‘smart water ecosystem’

- REWAISE is a major initiative of 4 European Water Utilities to implement technological innovations and new water governance methods
- After its first year, the project has deployed its first pilots to tackle key issues in improving water management efficiency
- Organised as Living Labs across Europe, each site develops specific solutions that are then implemented under a common methodology
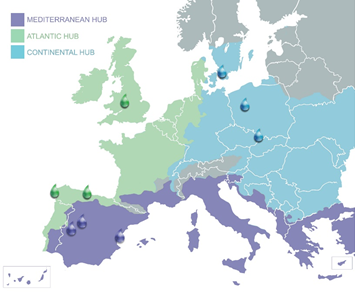
Picture: Living Labs agrupate in three Hubs
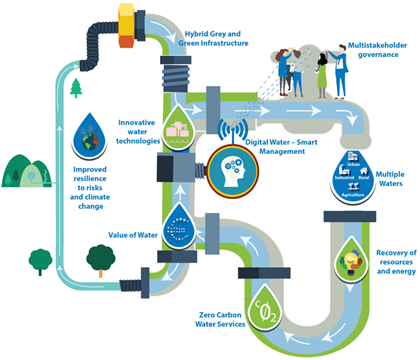
Comprising twenty-five entities from eleven different European countries, the Aqualia-led REWAISE has completed its maiden year. The aim of creating a ‘smart water ecosystem’ has already produced its first results. The first anniversary of this EU co-funded initiative was an opportunity to share the progress made during the 3rd General Assembly in Brussels.
REWAISE engages a network of living labs across Europe in three different climate zones (Mediterranean, Atlantic and Continental) to test technological innovations in real water environments.
Since the initiative’s inception, REWAISE entities have been forging a framework for decentralised water services, involving all relevant stakeholders with a view to achieving a sustainable water cycle and extracting the value of water from the initial demonstrative activities:
The Skaane Living Lab has already implemented two activities to recover resources. The first is an ultrafiltration pilot for roof-based rainwater harvesting installed in a public urban area with an underground storage of 100 m3. The pilot aims to reuse water for irrigation with a focus on the removal of microplastics and micropollutants.

Storm pond in Lund (SE)
In addition, the VASYD building now boasts the very first urine separation toilet prototype installed and monitored in this crowded working place to produce a new dry and safe fertiliser.
In the Galicia Living Lab, after a successful pilot run of an anaerobic bioreactor for treating 1 m3/day in Vigo, the design of a demo unit for sewer mining for treating 55 m3/day of wastewater from a local car factory has been completed. The unit is capable of repurposing water for cooling, washing and processing, transforming organic matter into biogas and also recovering nutrients for fertigation.
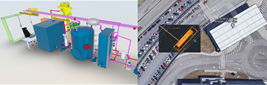
AnMBR pilot plant in Vigo and its location
In Vigo, new designs are also in the pipeline to create a large ultrafiltration plant for treating surface water following the successful pilot tests to compare membranes and define quality parameters.
The Midlands Living Lab is implementing network modelling and control, to reduce distribution leaks and prevent flooding in collection systems. Work is also underway to scale up and design the ammonia recovery unit based on stripping sludge dewatering liquors. Options are also being examined for generating hydrogen from the hydrolysis of concentrated ammonia.
The REWAISE IT platform is being developed to establish a common framework of digital innovation for supporting alternative water management strategies. One main challenge is finding tools to limit the need for thousands of sensors everywhere. Initial efforts are focusing on separate modelling of reservoirs and algae formation, a drinking water treatment plant and distribution system, sewage network and wastewater treatment plants so as to optimise operations before integrating the different modules.
Over 30 KPIs have been identified and categorised in different groups to benchmark project progress, namely technical, environmental, economic, and social key performance indicators. Having figures on carbon footprint, water scarcity and human toxicity will be useful for measuring the technical merits, while the number of market briefs, communication impacts, and economic analysis will assess the commercial value of the most promising technologies.
In this context, a map of key stakeholders has been developed to analyse the community and civil context of each Living Lab, to establish dialogues through hub-based competency groups. Guidelines to measure the impact of improved water services in terms of governance, and to determine the Social Return on Investment, will in turn help incentivise water-related investments, to accelerate SME growth by enhanced social engagement.
All this progress is coordinated with the other four EU co-funded initiatives within H2020 SC5-04-2019 call, grouped in a cluster baptised as Circular Smart Economy for Water (CirSEau). Three working groups were created to identify common methodologies for boosting i) Stakeholder engagement, ii) Communications, and iii) Impact and KPI assessment. Joint sessions were also held with the European Research Executive Agency (REA) to garner policy feedback for water directives.
REWAISE will be active for five years to implement its innovative processes in a sustainable water cycle. It posts the most recent events and advances on its website www.rewaise.eu.
https://twitter.com/REWAISE_EU
https://www.linkedin.com/company/rewaise-eu-project/
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCgKKjNbehcnSLzdqoCYokcA/featured







