Título: Neutron Star Formation in Accretion-Induced Collapse of White Dwarfs
Lugar: Seminario del DAA. Edificio Investigación Jeronimo Muñoz, planta cuarta, en Burjassot.
Día: Lunes 4 de diciembre de 2023.
Hora: 12:00.
Resumen:
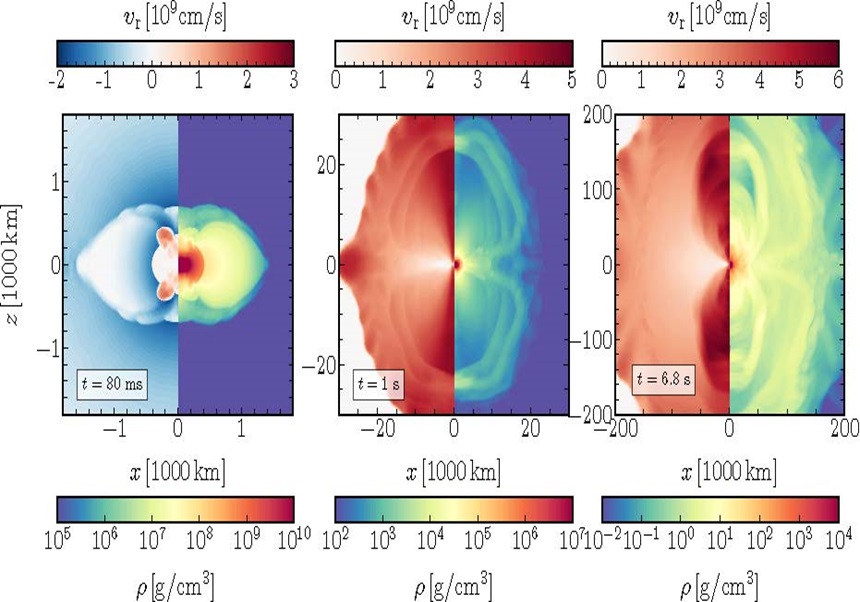
The accretion-induced collapse (AIC) of white dwarfs (WDs) is an alternative scenario to neutron star formation, apart from the massive stellar collapse, it can act as a site for heavy-element nucleosynthesis, and is a candidate for fast-evolving transients. We present the results of the first long-time evolution of AICs from the onset of the white dwarf collapse to the homologous expansion of the ejecta for a set of six models of non-rotating (1 model) and rotating (5 models) WDs with different initial masses, spin rates, and angular momentum profiles. Our simulations determine characteristic properties of the AIC events, such as ejecta masses and energy, ejecta geometry, the neutron-to-proton ratio, entropy, and expansion time scale of the ejecta. We demonstrated that AICs produce neutrino-driven outflows and are sub-energetic events with low explosion energies of ~ 0.1 Bethe. Our models yield outflows with a total ejecta mass of ~0.001 solar masses with a large spread in the neutron-to-proton ratio distribution and disfavor strong r-process nucleosynthesis. Our self-consistent dynamical simulations serve to predict the observational signatures of AIC events and their contribution to the production of heavy elements in the Universe.
Conexión remota: Enlace






