Feudalism was the ruling regime until XII century, when the first cities appeared
15 april 2016
Feudalism was the leading political system in Western Europe in the Middle Ages. It was based on the descentralization of power. The King or the Emperor was the pinnacle of power whereas the peasants were at the bottom. Peasants were subjected to the nobles, who occupied a middle position in the society and exerted power with autonomy and independence.
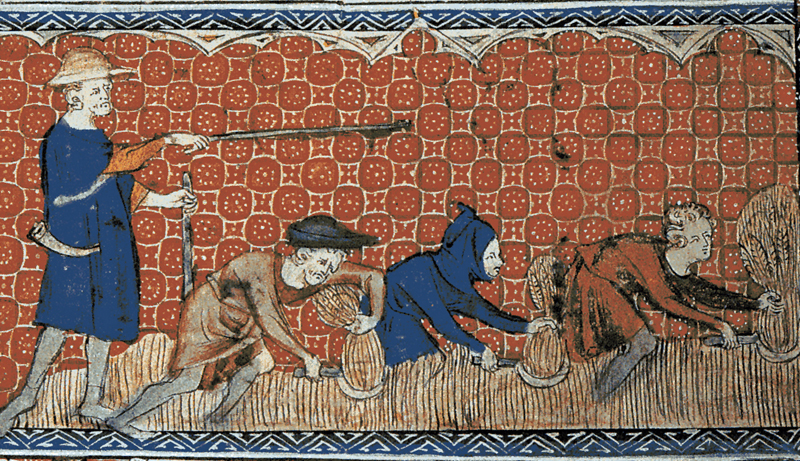
After a period of wars and a insecure and unstable atmosphere, free man had to be subjected to the noble man who ruled the land in which they lived, establishing a vassalage relationship. The vassal received a little portion of land in which he cultivated in order to supply himself. The vassal paid a rent to the noble who owned the land. In exchange, the noble provided a military protection. This reciprocal relationship was profitable for the noble man, who apart from taking a superior position, he also exerted a socially accepted coercion.
Peasants lives in the Middle Ages was very hard. It was based on the agriculture and the 90% of the farming were cereals. The agriculture was at a very early stage and it was focused on the immediate supplying. The nobility owned the land and they did not trust in newness, so the new agricultural techniques did not come until the end of XI century. Triennial rotation was introduced: the surface of the land was divided in three parts and the cultivations were rotating. One year wheat was cultivated, the following year; cereal. On the third year, the land rested. This way guaranteed better farmings for the land was not over-exploited.
Serf worked in order to maintain the clergy and the aristocracy, since in a feudal society they were at the lowest stratum. Despite the fact that they made most of the population in the Middle Ages, they had to maintain the rest of the stratums (clergy and aristocracy). When the agriculture improved in the rest of Europe, the situation changed: In the XII century, villages increased greatly, population grew as well as the production. The first concentrations of populations appeared: It was the origin of the cities.
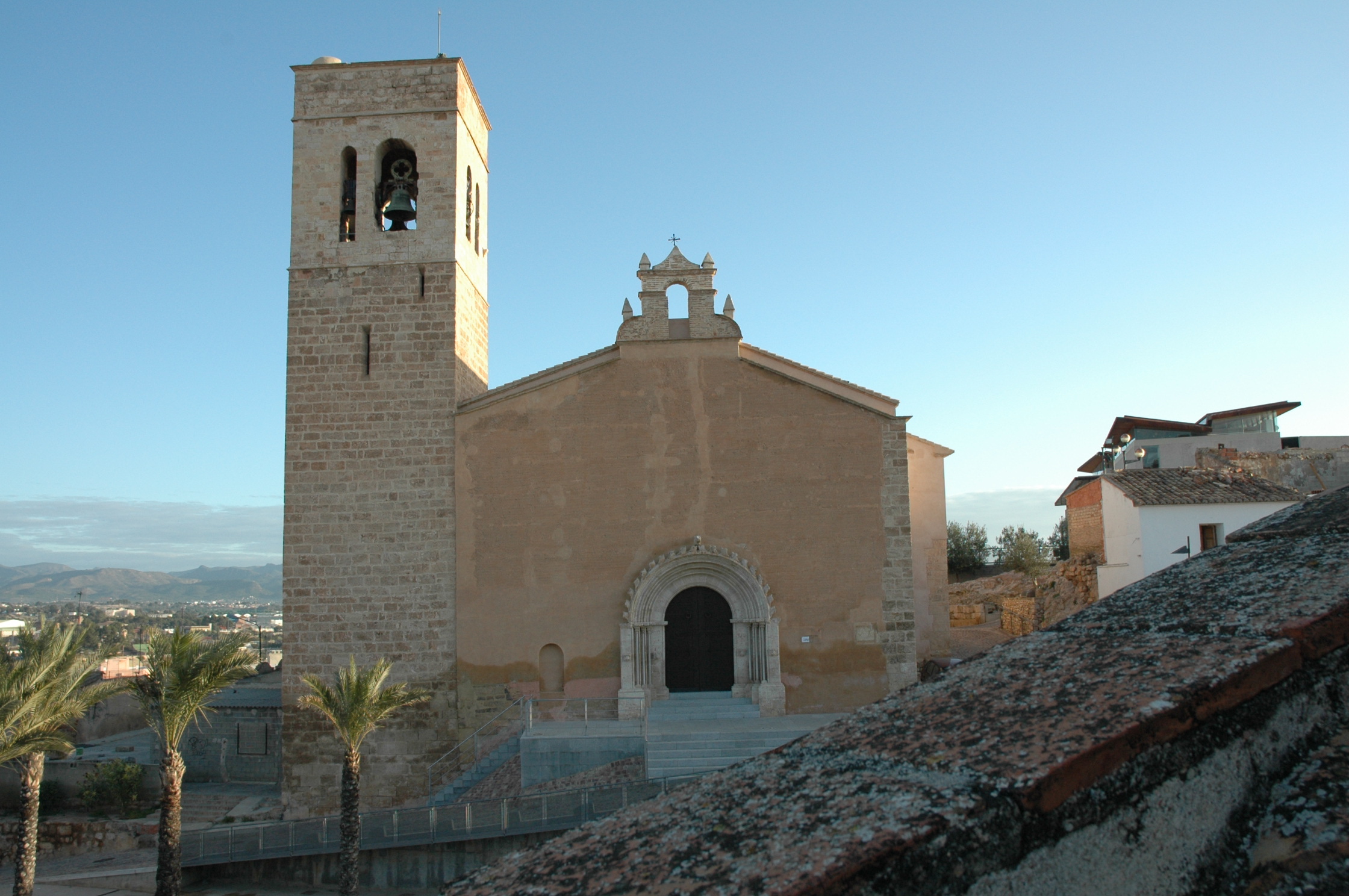
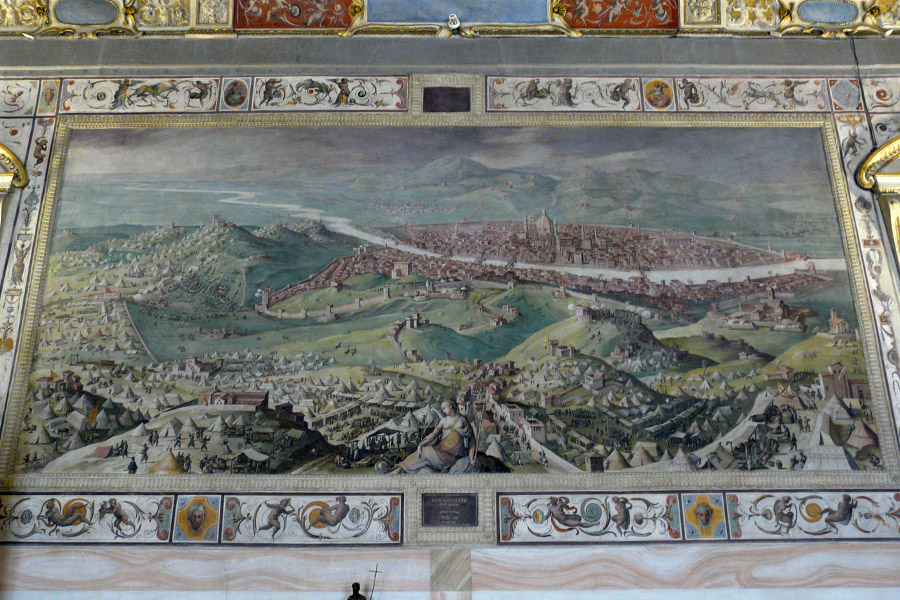
Most of Roman cities became ecclesiastical management centers and they were inside the manors of the feudal lords. It had sparse population but from XII century a great change happened: after the agricultural progresses population grew and that ment a higher economic development. Old Roman cities became awashed again and then the medieval city appeared. In XIII century some cities like Paris or Florence reached the 100 000 inhabitants.

Published by: Inés Luján









